News
What is the Salary of a Blockchain Developer? [2023 Edition]

How much do you know about blockchain? At the very least, you may be aware of its existence if you’ve ever heard or read anything about Bitcoin. If your knowledge of blockchain is a little light, then you’re about to learn a lot more about it. If you have heard of blockchain, then you need to check out why blockchain developer salary are going off the charts.
Understanding What Is Blockchain
Blockchain’s origins go back to 2008, as a means to power Bitcoin, which in turn came out a year later in 2009. A “block” is a means of permanently storing data, analogous to a page in a ledger, which, when created, cannot be altered or deleted. Members of the online community called “miners” maintain it, and when it’s linked with other blocks, you have a “Blockchain.”
Businesses and organizations today are rapidly adopting blockchain technology as a reliable means of keeping sensitive data safe. Blockchain’s miners earn Bitcoin for their efforts. Anyone can be a miner, provided they have the right tools to do it and the time to invest in the process.
Enroll in Front-End Developer Courses at Simplilearn and become a proficient web developer.
Check out the video below that will help you understand who is a Blockchain developer, types of Blockchain developers, steps to become a Blockchain developer, salaries offered to Blockchain developers and how companies are using Blockchain.
Who Is a Blockchain Developer?
In the global market, Blockchain has gained popularity due to its salient features. It is an append-only peer-to-peer network that maintains a cryptographically secure distributed ledger and that can only be updated through the consensus mechanisms such as BFT, PBFT, and so on. In the market, numerous IT organizations need blockchain developers. So being a blockchain developer is a smart choice because it is the most recent technology that one can master and advance in their career. There are two different types of blockchain developers, core and software blockchain developers. Core blockchain developers design the protocols, and maintain the existing blockchains, whereas blockchain software developers develop new blockchain applications, NFTs, and so on.
Different Types of Blockchain Developers and Their Roles
There are two different kinds of blockchain developers:
- Core blockchain developers design the architecture and security of a blockchain system
- Blockchain software developers use the core web foundation and architecture built by the core developer to create decentralized applications (dapps) and web applications, as well as smart contracts
Popularity of Blockchain
Blockchain provides an extremely secure method of storing data and conducting transactions. Worldwide spending on blockchain solutions is expected to grow from 1.5 billion in 2018 to an estimated 15.9 billion by 2023.
Furthermore, as the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to gain acceptance and usage, it is increasingly adopting blockchain technology. Forecasts suggest that by 2030 around 50 billion IoT devices will be in use around the world meaning good news for blockchain and greater demand for blockchain developers.
The above developments are hardly surprising. Blockchain offers unparalleled data security, as one of the biggest concerns today is cybercrime. As more of our daily activity migrates online, security becomes a more pressing issue. Blockchain stands ready to meet those security needs, but that means more developers are needed and, consequently, salary incentives will be more appealing.
In light of blockchain’s surge in popularity and increasing acceptance, here’s all you need to know about blockchain developer salary across the globe, as well as a list of blockchain developer jobs in those same regions.
Blockchain Developer Salary By Experience Level
It is often said in the industry that the salary of a developer depends upon the experience level that he/she possesses. Depending upon the seniority in the domain, employees are classified into different categories. Let us have a look at the salary given to different categories.
Blockchain Developer Salary: Complete Beginner
An employee is said to be a complete beginner if the person has 0 years of software experience and 0-1 year of blockchain technology experience. The salary in this case may be around ~$110,000 per year.
Blockchain Developer Salary: New Developer
An employee is considered to be a new developer if the person has 1-2 years of software experience and 0-1 year of blockchain technology experience. The salary in this case may be around ~$120,000 per year.
Blockchain Developer Salary: Experienced Developer
An employee is considered to be an experienced developer if the person has 2-4 years of software experience and 0-1 year of blockchain technology experience. The salary in this case could be around ~$124,000 per year.
Blockchain Developer Salary: Advanced Developer
An employee is considered to be an experienced developer if the person has 2-4 years of software experience and 0-1 year of blockchain technology experience. The salary in this case could be around ~$143,000 per year.
Blockchain Developer Salary: Blockchain Master
An employee is considered to be an experienced developer if the person has 6-10 years of software experience and 2-4 years of blockchain technology experience. The salary in this case could be around ~$153,000 per year.
Blockchain Developer Salary Based on Country
In one word: excellent! blockchain developer salary are taking off world-wide as demand for blockchain engineers and developers continues to soar. Blockchain developers can pull in a salary that is comparable with Artificial Intelligence (AI) developers, according to CNBC, and that’s some serious money!
Here are a few blockchain developer salary in different areas of the world. Bear in mind that these figures can fluctuate based on precise geographical location, company size, spikes in demand, and other factors.
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in India is over ₹460K
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in the US is over $96K
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in the UK is over £68,000
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in Singapore is around S$95,865
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in Canada is $95,000 CAD
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in Germany ranges from $60K to $150K
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in Switzerland is USD 180,000
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in Canada is C$136,500. Additionally, an entry-level position averages C$78,500
- Average annual salary of a blockchain developer in China ranges from Standard ¥45k to ¥60k, according to the Blockchain Council. Directors and managers earn approximately ¥60k to ¥120k.
Blockchain Developer Salary Based on Experience and Skills
Junior blockchain developers are typically assigned more supportive duties or groundwork. These tasks include debugging and repairing mobile apps, creating blockchain database application programming interfaces (API), or even handling the user interface (UI) design and front-end development of web and mobile applications. Think of them as entry-level developers, interns, or assistants.
To that end, their salaries run on the lower end, although even that starting pay is quite a bundle! For instance, ZipRecruiter shows an annual average salary of $120,748 for a junior blockchain developer in the United States. However with the right expertise and the skills a Blockahin developer can earn over $150K yearly.
Skills Required to Become a Blockchain Developer
To become a blockchain developer, one must gain knowledge or expertise in a variety of other computer sciences and mathematical domains, such as cryptography, etc.
1. Design of the Blockchain/ Blockchain Architecture
To train yourself to become a blockchain developer, understanding the basic concepts and terminologies in the field of blockchain is very important. Learn the fundamental concepts of blockchain, and also learn about real-time blockchain applications and the working mechanism of various consensus protocols.
2. Data Structures
Learning Data Structures strengthen your skill of understanding the problems at a wide level and help to provide an optimized solution within the constraints. They are also used to store data in an organized and efficient manner. Explore different types of data structures such as arrays, trees, and linked lists.
3. Cryptography
It is a method of securing sensitive data from unauthorized users, threats, and attacks. The fundamentals of computer science and mathematics serve as the foundation for developing cryptography protocols. In general, data is encrypted at the sender and decrypted at the receiver using various cryptographic techniques.
4. Smart Contract Development
This trendy technology enables Ethereum blockchain developers to code and develop a special type of transaction protocol called Smart Contracts. The objective of a smart contract is to simplify the transaction process between parties, restricting the participation of a third party and also cutting off the additional cost involved in it.
5. Web-Development
Learning some of the fundamentals of web development will be an added
advantage because with blockchain one can create DApps.
Responsibilities and Roles of Blockchain Developers
There are certain roles and responsibilities for a blockchain developer. Being a blockchain developer, one needs to focus on the strength of the network security protocol deployed in the peer-to-peer network. Some other responsibilities include conducting research and trying to improve the blockchain architecture, leading to bringing out some new applications. A blockchain developer must also ensure that the transactions are cryptographically secured.
Finding a Blockchain Developer Job
Blockchain developers are in high demand and earn a good salary. That’s great, the next question is how do you get one of these fantastic jobs and earn the best blockchain developer salary out there?
The internet is your greatest ally in the quest for finding the best blockchain developer salary and career opportunities. Although there are countless job-finding websites out there, the best sites for blockchain jobs are AngelList, Blockchainjobz, Blocktribe, Crypto Jobs List, Indeed.com, Joblift, Linkedin, and Upwork.
How to Become a Blockchain Developer?
Blockchain has been a trending technology across the globe due to the transparency it maintains in every transaction. Here are some steps to be followed to become a blockchain developer.
Step 1: Learn Basics
The first and major step is to learn the basics of blockchain and its applications. It is a prerequisite skill, without proper domain knowledge, one cannot proceed further in the blockchain industry.
Step 2: Start Coding
To become a developer in the domain of blockchain, one needs to be familiar with some of the programming languages. It is also recommended to learn some OOPS concepts. There are certain programming languages such as Solidity used to develop applications for blockchain technology.
Step 3: Understanding Smart Contracts
These are one of the most important applications of blockchain, which involves a piece of code that executes business logic. Its objective is to simplify the transaction.
Step 4: Keep Yourself Updated
Keep yourself updated by examining recent advancements in blockchain technology and trying to do more R&D work, which may help in designing new applications and improving the existing ones.
Factors that Influence the Salary of a Blockchain Developer
In any domain of work, for any position or role certain factors influence the salary of the developer. In this case, let’s have a look at factors that influence the salary of a blockchain developer.
Experience
In the IT industry, the higher the work experience, the higher the salary offered to the candidate by the company. With more experience, one can apply for a senior position in the organization.
Job Location
This is another important aspect that influences the salary of a developer. Working in advanced cities helps the employee have a high chance of a better salary.
Job Role
Within a particular domain, there might be different roles present. Such as smart contract developers, DApps developers, Network Security Analysts, and so on. Depending on the role and its importance, the salary varies.
Skillset
Among all other factors, skillset plays a key role in deciding the salary of a blockchain developer. A candidate with a proper and good skill set can earn more than those who do not possess the same.
How to Prepare for a Blockchain Interview
Blockchain is a trendy technology in the modern era. There has been an increase in craze for this technology and many large organizations are leaning toward this technology. Hence there is a need for many developers in the domain of blockchain. So there are certain skills to be learned and tips to be followed before attending a blockchain interview. Prepare well in all concepts of blockchain architecture and fundamentals. Get updated with the latest advancements in technology. Learn more about the applications of blockchain and have a clear understanding of computer networks, data systems, and so on.
Skills Needed to Master for a Blockchain Interview
Here are some of the skills needed to master for a blockchain interview.
Start with the Fundamentals of Blockchain
The first and major step is to learn the basics of blockchain and its Applications. It is a prerequisite skill, without proper domain knowledge, one cannot proceed further in the blockchain industry.
Improve Your Cross-discipline of Broad Skills
It is recommended to gain knowledge across other domains as well. It helps us in tackling problems in other domains with our skills and knowledge.
Learn About the Different Blockchain Platforms
Due to the advancement in blockchain technology, there are many platforms present in the market such as Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, Sawtooth, and so on. It will be an added advantage to learn about other blockchain platforms as well.
Learn to Couple Business With Technology
Getting expertise in technology doesn’t help nowadays. But combining the technical experience with business strategies helps the developers in building some state-of-the-art results in the domain.
Know About Distributed Ledgers and Decentralized Platforms as Well
As we all know, blockchain is a distributed ledger and a decentralized platform. It is better to learn more about the distributed ledges and their architectures. It will be helpful in developing the platforms and provision new applications to the market.
Understand Enterprise Business Processes
It is required to understand the entire business process while preparing for an interview. Procurement, logistics, distribution, supply chain, treasury operations, and other related areas require a fundamental understanding. It helps you in getting a better job in the industry.
Couple Creativity With Simplicity
There is a need to come up with solutions that are both creative and simple. More crucially, any application will benefit from the ability to generate a solution without adding complexity. Having too many complexities may confuse the end users as well.
Grasp How Blockchain Standards and Ecosystems Work
It is important to understand and keep a note of blockchain standards and the working mechanism of other ecosystems as well. Learn to deconstruct all of the structures of popular platforms to gain a better understanding
Improve Your Communication Skills
Other than the technical skills, companies also focus on the communication skills of the employee. It plays a key role when attending an interview. We often hear that candidates get rejected due to a lack of communication skills. To work with a team, in a collaborative environment one needs to improve communication skills.
Gain Knowledge of Different Development Tools
In today’s market, nothing will last forever. Every tool or technology gets updated from time to time. So there is a need to gain knowledge of different development tools to sustain the industry.
Tips for Cracking a Blockchain Interview
Here are some tips for cracking a blockchain interview. They are:
1. Study the Company
Before attending a blockchain interview, it is suggested to do some background research about the company. It helps in boosting confidence and also gives a clear idea about the roles and positions offered by the company. There are other advantages such as finding out about the research work, clients, work culture, and all other details of the organization.
2. Keep Your Skills Up-To-Date
The most important thing in any domain of the IT industry is to get ourselves updated with all required technologies. In present days, every technology is updated frequently in a similar way the expectations from the companies also raise a bit high. So to survive in the organization it is recommended to get your skills updated regularly.
3. Research Blockchain Questions
Just make a wild guess about what questions may be asked in the interview. Initially, prepare for the most frequently asked questions in the domain of blockchain. Read more about the interview experiences of other people on the internet.
4. Join a Community
Rather than working as a single person, it would be better if one joins a blockchain developers community. It is a place where people share their views and ideas about the latest technologies present in the market. Many people post their views and other details such as the interview experience which will help us in preparing for one such interview.
5. Think Before Answering
Don’t get worried, after looking at the interviewer and the questions being asked. Maintain a clear state of mind and think before answering the questions. Hear the question clearly and answer it to the point.
6. Focus on Body Language and Speaking Voice
Speak with great confidence in your voice. Be bold and dare enough to tell the true answers. Never try to say fake answers, which may not be suitable for an interview. There must be a steady and subtle body language maintained throughout the interview.
7. Attend Mock Interviews
Practice more by attending more mock interviews. Attending mock interviews helps us to boost our self-confidence. We lose the fear of attending the interview and can face it with a brave heart.
The Ultimate Way to Become a Blockchain Developer
After reading about all of the opportunities and benefits of being a blockchain developer, (and also the lucrative blockchain developer salary) it wouldn’t be surprising to hear that you’re pondering a career change. If that’s where you find yourself, you’ll be glad to know that Simplilearn can help you get your start.
The Blockchain Certification Training Course provides an overview of Bitcoin, Hyperledger, Ethereum, and Multichain blockchain platforms. In this course, you’ll get to know and use tools like Ganache, Truffle, Meta Mask, and Geth to build Blockchain applications, learn how to set up a private Blockchain network using Hyperledger Composer, and deploy smart contracts on Ethereum. The certificate that you earn tells an employer that you are well-versed in this new technology and can be confidently expected to meet all of the demands that the position makes. Whether it’s blockchain or any other IT tool or concept, certification gives you an edge over the competition.
Even if you’re already working as a blockchain developer, there is always the option of upskilling, and increasing your salary potential. Blockchain technology is making inroads into a wide range of industries. Smart professionals plan and stay informed of the current technology; those are the people who succeed and climb the corporate ladder. So check out the course today and be a cutting-edge developer!
News
An enhanced consensus algorithm for blockchain
The introduction of the link and reputation evaluation concepts aims to improve the stability and security of the consensus mechanism, decrease the likelihood of malicious nodes joining the consensus, and increase the reliability of the selected consensus nodes.
The link model structure based on joint action
Through the LINK between nodes, all the LINK nodes engage in consistent activities during the operation of the consensus mechanism. The reputation evaluation mechanism evaluates the trustworthiness of nodes based on their historical activity status throughout the entire blockchain. The essence of LINK is to drive inactive nodes to participate in system activities through active nodes. During the stage of selecting leader nodes, nodes are selected through self-recommendation, and the reputation evaluation of candidate nodes and their LINK nodes must be qualified. The top 5 nodes of the total nodes are elected as leader nodes through voting, and the nodes in their LINK status are candidate nodes. In the event that the leader node goes down, the responsibility of the leader node is transferred to the nodes in its LINK through the view-change. The LINK connection algorithm used in this study is shown in Table 2, where LINKm is the linked group and LINKP is the percentage of linked nodes.
Table 2 LINK connection algorithm.
Node type
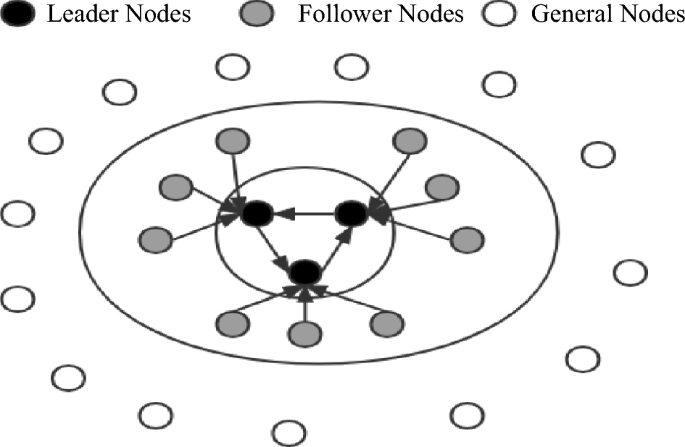
This paper presents a classification of nodes in a blockchain system based on their functionalities. The nodes are divided into three categories: leader nodes (LNs), follower nodes (FNs), and general nodes (Ns). The leader nodes (LNs) are responsible for producing blocks and are elected through voting by general nodes. The follower nodes (FNs) are nodes that are linked to leader nodes (LNs) through the LINK mechanism and are responsible for validating blocks. General nodes (N) have the ability to broadcast and disseminate information, participate in elections, and vote. The primary purpose of the LINK mechanism is to act in combination. When nodes are in the LINK, there is a distinction between the master and slave nodes, and there is a limit to the number of nodes in the LINK group (NP = {n1, nf1, nf2 ……,nfn}). As the largest proportion of nodes in the system, general nodes (N) have the right to vote and be elected. In contrast, leader nodes (LNs) and follower nodes (FNs) do not possess this right. This rule reduces the likelihood of a single node dominating the block. When the system needs to change its fundamental settings due to an increase in the number of nodes or transaction volume, a specific number of current leader nodes and candidate nodes need to vote for a reset. Subsequently, general nodes need to vote to confirm this. When both confirmations are successful, the new basic settings are used in the next cycle of the system process. This dual confirmation setting ensures the fairness of the blockchain to a considerable extent. It also ensures that the majority holds the ultimate decision-making power, thereby avoiding the phenomenon of a small number of nodes completely controlling the system.
After the completion of a governance cycle, the blockchain network will conduct a fresh election for the leader and follower nodes. As only general nodes possess the privilege to participate in the election process, the previous consortium of leader and follower nodes will lose their authorization. In the current cycle, they will solely retain broadcasting and receiving permissions for block information, while their corresponding incentives will also decrease. A diagram illustrating the node status can be found in Fig. 1.
Election method
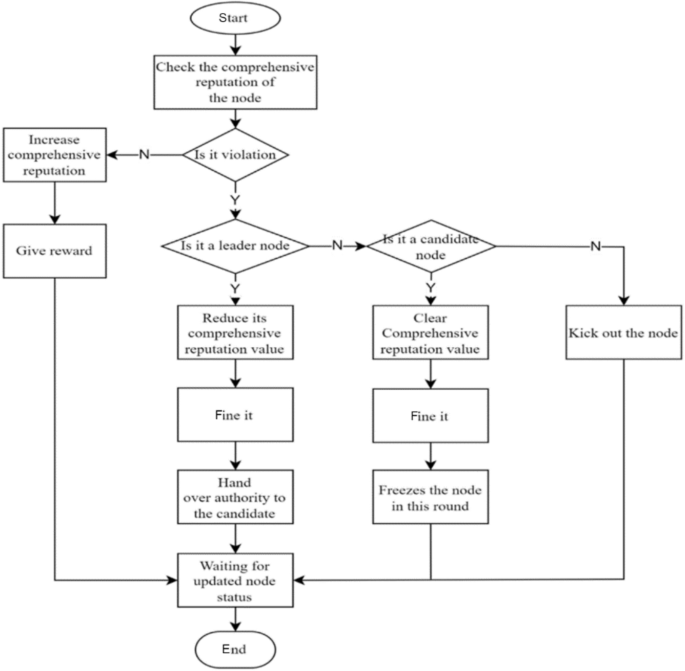
The election method adopts the node self-nomination mode. If a node wants to participate in an election, it must form a node group with one master and three slaves. One master node group and three slave node groups are inferred based on experience in this paper; these groups can balance efficiency and security and are suitable for other project collaborations. The successfully elected node joins the leader node set, and its slave nodes enter the follower node set. Considering the network situation, the maximum threshold for producing a block is set to 1 s. If the block fails to be successfully generated within the specified time, it is regarded as a disconnected state, and its reputation score is deducted. The node is skipped, and in severe cases, a view transformation is performed, switching from the master node to the slave node and inheriting its leader’s rights in the next round of block generation. Although the nodes that become leaders are high-reputation nodes, they still have the possibility of misconduct. If a node engages in misconduct, its activity will be immediately stopped, its comprehensive reputation score will be lowered, it will be disqualified from participating in the next election, and its equity will be reduced by 30%. The election process is shown in Fig. 2.
Incentives and penalties
To balance the rewards between leader nodes and ordinary nodes and prevent a large income gap, two incentive/penalty methods will be employed. First, as the number of network nodes and transaction volume increase, more active nodes with significant stakes emerge. After a prolonged period of running the blockchain, there will inevitably be significant class distinctions, and ordinary nodes will not be able to win in the election without special circumstances. To address this issue, this paper proposes that rewards be reduced for nodes with stakes exceeding a certain threshold, with the reduction rate increasing linearly until it reaches zero. Second, in the event that a leader or follower node violates the consensus process, such as by producing a block out of order or being unresponsive for an extended period, penalties will be imposed. The violation handling process is illustrated in Fig. 3.
Violation handling process.
Comprehensive reputation evaluation and election mechanism based on historical transactions
This paper reveals that the core of the DPoS consensus mechanism is the election process. If a blockchain is to run stably for a long time, it is essential to consider a reasonable election method. This paper proposes a comprehensive reputation evaluation election mechanism based on historical records. The mechanism considers the performance indicators of nodes in three dimensions: production rate, tokens, and validity. Additionally, their historical records are considered, particularly whether or not the nodes have engaged in malicious behavior. For example, nodes that have ever been malicious will receive low scores during the election process unless their overall quality is exceptionally high and they have considerable support from other nodes. Only in this case can such a node be eligible for election or become a leader node. The comprehensive reputation score is the node’s self-evaluation score, and the committee size does not affect the computational complexity.
Moreover, the comprehensive reputation evaluation proposed in this paper not only is a threshold required for node election but also converts the evaluation into corresponding votes based on the number of voters. Therefore, the election is related not only to the benefits obtained by the node but also to its comprehensive evaluation and the number of voters. If two nodes receive the same vote, the node with a higher comprehensive reputation is given priority in the ranking. For example, in an election where node A and node B each receive 1000 votes, node A’s number of stake votes is 800, its comprehensive reputation score is 50, and only four nodes vote for it. Node B’s number of stake votes is 600, its comprehensive reputation score is 80, and it receives votes from five nodes. In this situation, if only one leader node position remains, B will be selected as the leader node. Displayed in descending order of priority as comprehensive credit rating, number of voters, and stake votes, this approach aims to solve the problem of node misconduct at its root by democratizing the process and subjecting leader nodes to constraints, thereby safeguarding the fundamental interests of the vast majority of nodes.
Comprehensive reputation evaluation
This paper argues that the election process of the DPoS consensus mechanism is too simplistic, as it considers only the number of election votes that a node receives. This approach fails to comprehensively reflect the node’s actual capabilities and does not consider the voters’ election preferences. As a result, nodes with a significant stake often win and become leader nodes. To address this issue, the comprehensive reputation evaluation score is normalized considering various attributes of the nodes. The scoring results are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Comprehensive reputation evaluation.
Since some of the evaluation indicators in Table 3 are continuous while others are discrete, different normalization methods need to be employed to obtain corresponding scores for different indicators. The continuous indicators include the number of transactions/people, wealth balance, network latency, network jitter, and network bandwidth, while the discrete indicators include the number of violations, the number of successful elections, and the number of votes. The value range of the indicator “number of transactions/people” is (0,1), and the value range of the other indicators is (0, + ∞). The equation for calculating the “number of transactions/people” is set as shown in Eq. (1).
$$A_{1} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}l} {0,} \hfill & {{\text{G}} = 0} \hfill \\ {\frac{{\text{N}}}{{\text{G}}}*10,} \hfill & {{\text{G}} > 0} \hfill \\ \end{array} } \right.$$
(1)
where N represents the number of transactional nodes and G represents the number of transactions. It reflects the degree of connection between the node and other nodes. Generally, nodes that transact with many others are safer than those with a large number of transactions with only a few nodes. The limit value of each item, denoted by x, is determined based on the situation and falls within the specified range, as shown in Eq. (2). The wealth balance and network bandwidth indicators use the same function to set their respective values.
$${A}_{i}=20*\left(\frac{1}{1+{e}^{-{a}_{i}x}}-0.5\right)$$
(2)
where x indicates the value of this item and expresses the limit value.
In Eq. (3), x represents the limited value of this indicator. The lower the network latency and network jitter are, the higher the score will be.
The last indicators, which are the number of violations, the number of elections, and the number of votes, are discrete values and are assigned different scores according to their respective ranges. The scores corresponding to each count are shown in Table 4.
$$A_{3} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}l} {10*\cos \frac{\pi }{200}x,} \hfill & {0 \le x \le 100} \hfill \\ {0,} \hfill & {x > 100} \hfill \\ \end{array} } \right.$$
(3)
Table 4 Score conversion.
The reputation evaluation mechanism proposed in this paper comprehensively considers three aspects of nodes, wealth level, node performance, and stability, to calculate their scores. Moreover, the scores obtain the present data based on historical records. Each node is set as an M × N dimensional matrix, where M represents M times the reputation evaluation score and N represents N dimensions of reputation evaluation (M < = N), as shown in Eq. (4).
$${\text{N}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}c} {a_{11} } & \cdots & {a_{1n} } \\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ {a_{m1} } & \cdots & {a_{mn} } \\ \end{array} } \right)$$
(4)
The comprehensive reputation rating is a combined concept related to three dimensions. The rating is set after rating each aspect of the node. The weight w and the matrix l are not fixed. They are also transformed into matrix states as the position of the node in the system changes. The result of the rating is set as the output using Eq. (5).
$$\text{T}=\text{lN}{w}^{T}=\left({l}_{1}\dots {\text{l}}_{\text{m}}\right)\left(\begin{array}{ccc}{a}_{11}& \cdots & {a}_{1n}\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ {a}_{m1}& \cdots & {a}_{mn}\end{array}\right){\left({w}_{1}\dots {w}_{n}\right)}^{T}$$
(5)
Here, T represents the comprehensive reputation score, and l and w represent the correlation coefficient. Because l is a matrix of order 1*M, M is the number of times in historical records, and M < = N is set, the number of dimensions of l is uncertain. Set the term l above to add up to 1, which is l1 + l2 + …… + ln = 1; w is also a one-dimensional matrix whose dimension is N*1, and its purpose is to act as a weight; within a certain period of time, w is a fixed matrix, and w will not change until the system changes the basic settings.
Assume that a node conducts its first comprehensive reputation rating, with no previous transaction volume, violations, elections or vote. The initial wealth of the node is 10, the latency is 50 ms, the jitter is 100 ms, and the network bandwidth is 100 M. According to the equation, the node’s comprehensive reputation rating is 41.55. This score is relatively good at the beginning and gradually increases as the patient participates in system activities continuously.
Voting calculation method
To ensure the security and stability of the blockchain system, this paper combines the comprehensive reputation score with voting and randomly sorts the blocks, as shown in Eqs. (3–6).
$$Z=\sum_{i=1}^{n}{X}_{i}+nT$$
(6)
where Z represents the final election score, Xi represents the voting rights earned by the node, n is the number of nodes that vote for this node, and T is the comprehensive reputation score.
The voting process is divided into stake votes and reputation votes. The more reputation scores and voters there are, the more total votes that are obtained. In the early stages of blockchain operation, nodes have relatively few stakes, so the impact of reputation votes is greater than that of equity votes. This is aimed at selecting the most suitable node as the leader node in the early stage. As an operation progresses, the role of equity votes becomes increasingly important, and corresponding mechanisms need to be established to regulate it. The election vote algorithm used in this paper is shown in Table 5.
Table 5 Election vote counting algorithm.
This paper argues that the election process utilized by the original DPoS consensus mechanism is overly simplistic, as it relies solely on the vote count to select the node that will oversee the entire blockchain. This approach cannot ensure the security and stability of the voting process, and if a malicious node behaves improperly during an election, it can pose a significant threat to the stability and security of the system as well as the safety of other nodes’ assets. Therefore, this paper proposes a different approach to the election process of the DPoS consensus mechanism by increasing the complexity of the process. We set up a threshold and optimized the vote-counting process to enhance the security and stability of the election. The specific performance of the proposed method was verified through experiments.
The election cycle in this paper can be customized, but it requires the agreement of the blockchain committee and general nodes. The election cycle includes four steps: node self-recommendation, calculating the comprehensive reputation score, voting, and replacing the new leader. Election is conducted only among general nodes without affecting the production or verification processes of leader nodes or follower nodes. Nodes start voting for preferred nodes. If they have no preference, they can use the LINK mechanism to collaborate with other nodes and gain additional rewards.
View changes
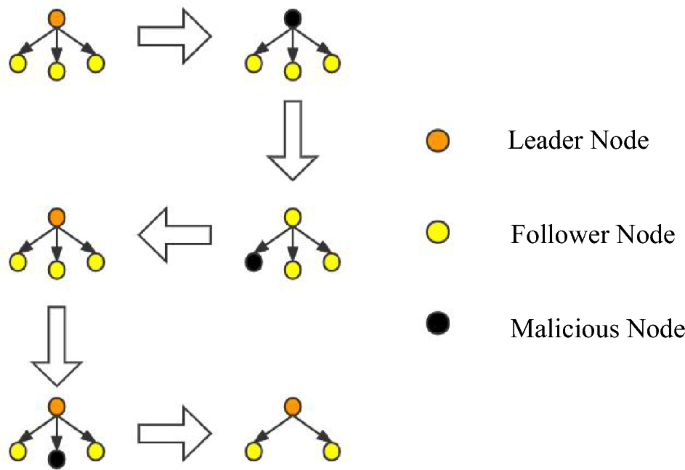
During the consensus process, conducting a large number of updates is not in line with the system’s interests, as the leader node (LN) and follower node (FN) on each node have already been established. Therefore, it is crucial to handle problematic nodes accurately when issues arise with either the LN or FN. For instance, when a node fails to perform its duties for an extended period or frequently fails to produce or verify blocks within the specified time range due to latency, the system will precisely handle them. For leader nodes, if they engage in malicious behavior such as producing blocks out of order, the behavior is recorded, and their identity as a leader node is downgraded to a follower node. The follower node inherits the leader node’s position, and the nature of their work is transformed as they swap their responsibilities of producing and verifying blocks with their original work. This type of behavior will not significantly affect the operation of the blockchain system. Instead of waiting until the end of the current committee round to punish malicious nodes, dynamic punishment is imposed on the nodes that affect the operation of the blockchain system to maintain system security. The view change operation is illustrated in Fig. 4.
In traditional PBFT, view changes are performed according to the view change protocol by changing the view number V to the next view number V + 1. During this process, nodes only receive view change messages and no other messages from other nodes. In this paper, the leader node group (LN) and follower node group (FN) are selected through an election of the LINK group. The node with LINKi[0] is added to the LN leader node group, while the other three LINK groups’ follower nodes join the FN follower node group since it is a configuration pattern of one master and three slaves. The view change in this paper requires only rearranging the node order within the LINK group to easily remove malicious nodes. Afterward, the change is broadcast to other committee nodes, and during the view transition, the LINK group does not receive block production or verification commands from the committee for stability reasons until the transition is completed.
News
The Hype Around Blockchain Mortgage Has Died Down, But This CEO Still Believes

LiquidFi Founder Ian Ferreira Sees Huge Potential in Blockchain Despite Hype around technology is dead.
“Blockchain technology has been a buzzword for a long time, and it shouldn’t be,” Ferriera said. “It should be a technology that lives in the background, but it makes everything much more efficient, much more transparent, and ultimately it saves costs for everyone. That’s the goal.”
Before founding his firm, Ferriera was a portfolio manager at a hedge fund, a job that ended up revealing “interesting intricacies” related to the mortgage industry.
Being a mortgage trader opened Ferriera’s eyes to a lot of the operational and infrastructure problems that needed to be solved in the mortgage-backed securities industry, he said. That later led to the birth of LiquidFi.
“The point of what we do is to get raw data attached to a resource [a loan] on a blockchain so that it’s provable. You reduce that trust problem because you have the data, you have the document associated with that data,” said the LiquidFi CEO.
Ferriera spoke with National Mortgage News about the value of blockchain technology, why blockchain hype has fizzled out, and why it shouldn’t.
News
New bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work

The Department of Veterans Affairs would have to evaluate how blockchain technology could be used to improve benefits and services offered to veterans, according to a legislative proposal introduced Tuesday.
The bill, sponsored by Rep. Nancy Mace, R-S.C., would direct the VA to “conduct a comprehensive study of the feasibility, potential benefits, and risks associated with using distributed ledger technology in various programs and services.”
Distributed ledger technology, including blockchain, is used to protect and track information by storing data across multiple computers and keeping a record of its use.
According to the text of the legislation, which Mace’s office shared exclusively with Nextgov/FCW ahead of its publication, blockchain “could significantly improve benefits allocation, insurance program management, and recordkeeping within the Department of Veterans Affairs.”
“We need to bring the federal government into the 21st century,” Mace said in a statement. “This bill will open the door to research on improving outdated systems that fail our veterans because we owe it to them to use every tool at our disposal to improve their lives.”
Within one year of the law taking effect, the Department of Veterans Affairs will be required to submit a report to the House and Senate Veterans Affairs committees detailing its findings, as well as the benefits and risks identified in using the technology.
The mandatory review is expected to include information on how the department’s use of blockchain could improve the way benefits decisions are administered, improve the management and security of veterans’ personal data, streamline the insurance claims process, and “increase transparency and accountability in service delivery.”
The Department of Veterans Affairs has been studying the potential benefits of using distributed ledger technology, with the department emission a request for information in November 2021 seeking input from contractors on how blockchain could be leveraged, in part, to streamline its supply chains and “secure data sharing between institutions.”
The VA’s National Institute of Artificial Intelligence has also valued the use of blockchain, with three of the use cases tested during the 2021 AI tech sprint focused on examining its capabilities.
Mace previously introduced a May bill that would direct Customs and Border Protection to create a public blockchain platform to store and share data collected at U.S. borders.
Lawmakers also proposed additional measures that would push the Department of Veterans Affairs to consider adopting other modernized technologies to improve veteran services.
Rep. David Valadao, R-Calif., introduced legislation in June that would have directed the department to report to lawmakers on how it plans to expand the use of “certain automation tools” to process veterans’ claims. The House of Representatives Subcommittee on Disability Assistance and Memorial Affairs gave a favorable hearing on the congressman’s bill during a Markup of July 23.
News
California DMV Uses Blockchain to Fight Auto Title Fraud

TDR’s Three Takeaways: California DMV Uses Blockchain to Fight Fraud
- California DMV uses blockchain technology to manage 42 million auto titles.
- The initiative aims to improve safety and reduce car title fraud.
- The immutable nature of blockchain ensures accurate and tamper-proof records.
The California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) is implementing blockchain technology to manage and secure 42 million auto titles. This innovative move aims to address and reduce the persistent problem of auto title fraud, a problem that costs consumers and the industry millions of dollars each year. By moving to a blockchain-based system, the DMV is taking advantage of the technology’s key feature: immutability.
Blockchain, a decentralized ledger technology, ensures that once a car title is registered, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This creates a highly secure and transparent system, significantly reducing the risk of fraudulent activity. Every transaction and update made to a car title is permanently recorded on the blockchain, providing a complete and immutable history of the vehicle’s ownership and status.
As first reported by Reuters, the DMV’s adoption of blockchain isn’t just about preventing fraud. It’s also aimed at streamlining the auto title process, making it more efficient and intuitive. Traditional auto title processing involves a lot of paperwork and manual verification, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Blockchain technology automates and digitizes this process, reducing the need for physical documents and minimizing the chances of errors.
Additionally, blockchain enables faster verification and transfer of car titles. For example, when a car is sold, the transfer of ownership can be done almost instantly on the blockchain, compared to days or even weeks in the conventional system. This speed and efficiency can benefit both the DMV and the vehicle owners.
The California DMV’s move is part of a broader trend of government agencies exploring blockchain technology to improve their services. By adopting this technology, the DMV is setting a precedent for other states and industries to follow, showcasing blockchain’s potential to improve safety and efficiency in public services.
-
 Ethereum11 months ago
Ethereum11 months agoEthereum Posts First Consecutive Monthly Losses Since August 2023 on New ETFs
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoCryptocurrency Regulation in Slovenia 2024
-

 News11 months ago
News11 months agoNew bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoThink You Own Your Crypto? New UK Law Would Ensure It – DL News
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoUpbit, Coinone, Bithumb Face New Fees Under South Korea’s Cryptocurrency Law
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoA Blank Slate for Cryptocurrencies: Kamala Harris’ Regulatory Opportunity
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoBahamas Passes Cryptocurrency Bill Designed to Prevent FTX, Terra Disasters
-

 Regulation11 months ago
Regulation11 months agoIndia to Follow G20 Policy for Cryptocurrency Regulation: MoS Finance
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago“Captain Tsubasa – RIVALS” launches on Oasys Blockchain
-

 News11 months ago
News11 months agoEU supports 15 startups to fight online disinformation with blockchain
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto