Regulation
Global Cryptocurrency Regulations – Wild West to Outright Ban
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital asset that operates on a blockchain. A blockchain is a public ledger of transactions that’s visible to anyone and does not rely on a central authority. Unlike cash, crypto is impossible to counterfeit because it uses cryptography for transaction verification.
The first crypto, Bitcoin, emerged in 2009. Its creator, known by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, wanted to create a currency free from government or bank control.
This concept appeals to those who prefer privacy in their transactions and distrust traditional financial institutions.

Crypto’s accessibility has sparked crypto adoption in developing countries.
Fast and borderless transactions are another reason for using crypto.
There’s no need for a bank account – anyone can access their crypto wallet with an internet connection.
There are thousands of cryptocurrencies, each with its own features and purposes. Some act as payment methods, others as long-term stores of value, similar to gold.
Utility tokens unlock specific features within a project, while meme coins are created for fun and quick gains (or losses) on speculation.
What Does Regulation for Cryptocurrency Mean?
Cryptocurrencies operate outside the traditional financial system, allowing anyone with an internet connection to make payments globally.
Governments try to catch up with this new asset class and gain some control by establishing legal frameworks. These regulations are all over the place, differing wildly between countries and constantly evolving.
But why regulate something that was created to bypass regulations? Well, it’s not that simple. Here are some of the reasons.
Crypto’s anonymity can be a double-edged sword
Regulations aim to crack down on illicit activities like money laundering and tax evasion. For example, centralized crypto exchanges must verify user identities and monitor transactions for suspicious activity.
To create a fair environment for investors
Blockchain regulation strives to create a level playing field by preventing artificial price inflation and weeding out scams through licensing laws.
For tax purposes
Governments can treat crypto as property, securities, or something else to specify how capital gains, losses, and income generated from crypto activities are taxed.
To build investor confidence
Consumer protection laws encourage more people to participate in trade, increasing market liquidity and tax revenue.
To counter volatility
Dramatic crypto price swings can cause tremors in the broader financial system. Regulations act like an anchor, preventing sudden price drops that might force investors to flee to safer havens.
To foster innovation safely
Regulations outline how companies can experiment with blockchain technology and raise capital while protecting investors from fraudulent offerings.
Consequently, crypto legislation might encompass the following:
- Licensing and registration of crypto exchanges, custodians (services that hold your crypto for you), and initial coin offering (ICO) platforms
- Know your customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) procedures to verify user identities and monitor transactions to prevent financial crime
- Consumer protections, like risk disclosures, limitations on misleading marketing practices, and dispute resolution procedures
- Taxation, for example, some countries don’t collect any tax on crypto transactions, whereas others tax crypto as capital gains
Some governments employ extensive regulations for crypto businesses. For example, Japan enforces strict KYC, taxation, consumer protection, and licensing rules. Others have almost none.
Likewise, some governments encourage crypto trading and blockchain development, while others, like China, ban it entirely. That’s why you should do your due diligence before engaging in any crypto-related activity.
Naturally, such disparity can challenge global trade. This is where the International Monetary Fund (IMF), an international organization with 190 member countries, comes into play.


There’s no one-size-fits-all ‘IMF crypto law.’ Instead, the IMF gives individual countries policy recommendations and encourages them to cooperate. We can only hope that its members will eventually reach a consensus.
How is Crypto Regulated in the United States?
Now that you know the reasons behind digital asset laws, let’s unpack specific US crypto regulations.
The US regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency is a work in progress. The emergence of Bitcoin caught authorities off guard. There were absolutely no laws governing virtual currencies, which created grounds for speculation and manipulation.
As crypto gained popularity, the US government appointed three agencies to oversee the market and protect investors.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
The SEC focuses on securities – crypto investments made to raise capital. Therefore, cryptocurrencies that function as a medium of exchange or utility tokens don’t count as securities.
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
The CFTC oversees derivatives markets. Put simply, derivatives are financial instruments whose value depends on the underlying asset. For example, if you believe Bitcoin’s ($BTC) price will rise, you could enter into a futures contract with another investor.
In this contract, you agree to buy or sell $BTC at a set price on a specific date. You make a profit if the $BTC price goes up by that date. In this case, $BTC is the underlying asset, and the futures contract derives its value from $BTC price fluctuations.
Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
The IRS is interested in crypto’s tax implications and requires US residents to report gains and losses on trading activities.
Apart from these three big players, the US government may involve the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in investigating money laundering cases.
Naturally, navigating the various regulations from each of these agencies can be overwhelming. Here are the key points you should know about crypto taxation in the US.
You must pay capital gains tax when selling cryptoYour losses can offset the gainsMining rewards are taxed as ordinary incomeThe IRS is watching
The tax rate depends on your tax bracket and how long you held the cryptocurrency before selling. Short-term gains (held for less than a year) are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term gains typically are subject to lower tax rates.
Say you lost $8K during a bear market. You can use this loss to reduce your taxable capital gains from other investments. It’s worth noting that there’s a $3K capital loss cap for single tax filers.
Remember to report them on your tax return! What’s more, President Joe Biden recently proposed imposing a 30% electricity tax on mining. While the law is not yet in place, it highlights that crypto regulations in the US constantly evolve.
Just because crypto transactions are anonymous doesn’t mean that your activities are invisible. Centralized exchanges (CEXs) must comply with KYC procedures and report to the IRS.


While it may seem like the US government is only concerned with getting its cut, it also introduces investor protections:
- The SEC mandates transparent disclosures to reduce the risk of fraud. This includes details about the project, the team’s background, and the risks involved in investing.
- SEC offers educational resources to help investors understand crypto fundamentals, identify red flags, and make informed investment decisions.
- KYC rules help exchanges identify suspicious activities that may harm other users.
Also worth mentioning is that some states may have specific laws on crypto. For example, New York has a specific licensing regime called the ‘BitLicense’ for businesses dealing with virtual currencies.
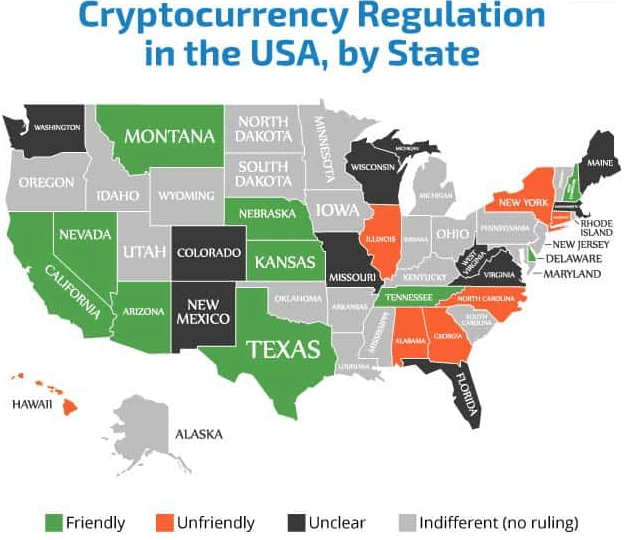

Source: Finance Magnates
This license requires extensive background checks, compliance measures, and cybersecurity protocols. Likewise, California requires a Money Transmitter License for businesses that process over $10k in crypto within a year.
These are just a few examples, so always DYOR. You can find state-specific information on the North American Securities Administrators Association (NASAA) website.
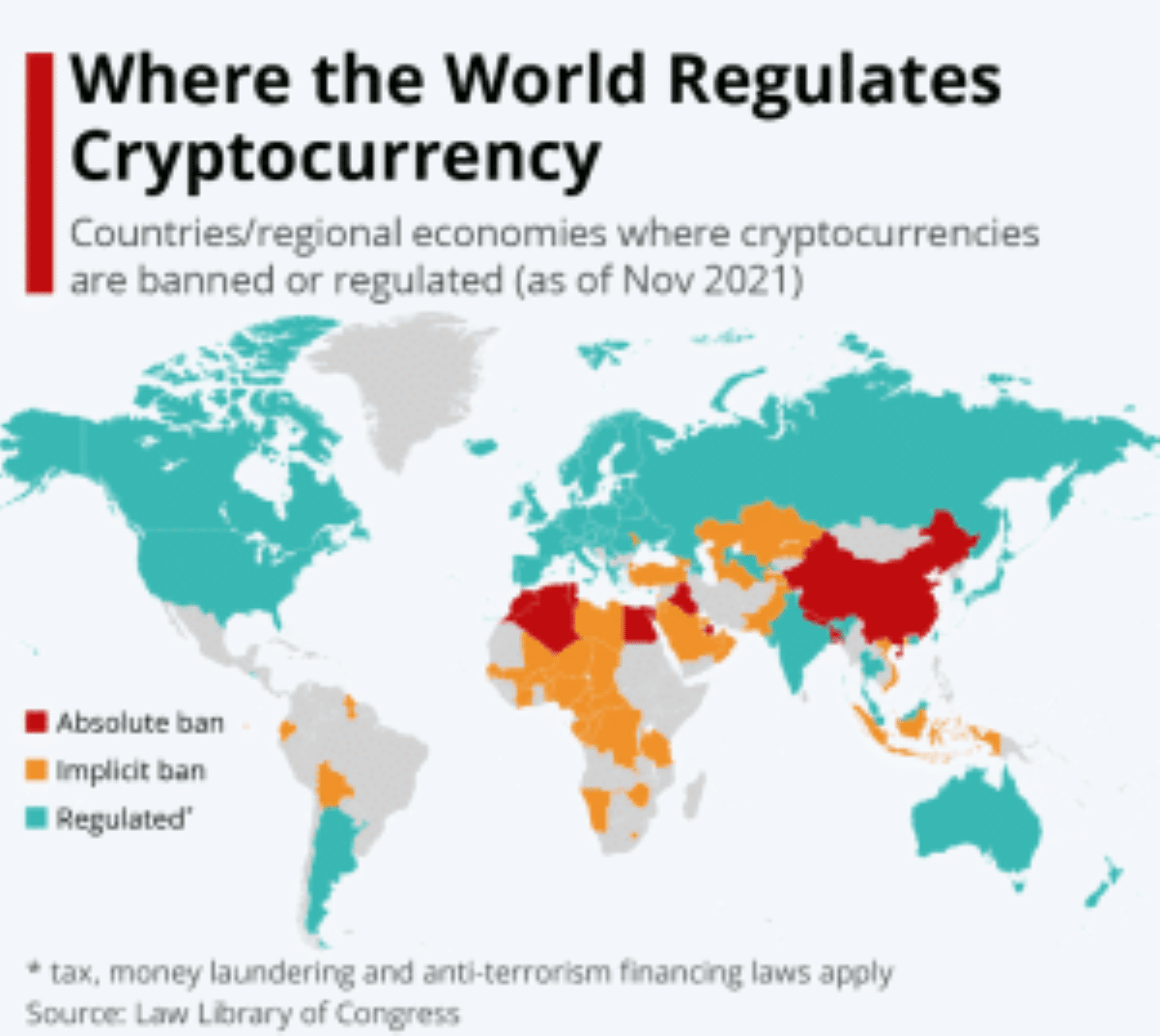
Rules and Regulations for Cryptocurrency Around the World
Crypto transcends borders, but regulations don’t. Read on to discover how the rules of the game differ across the world.
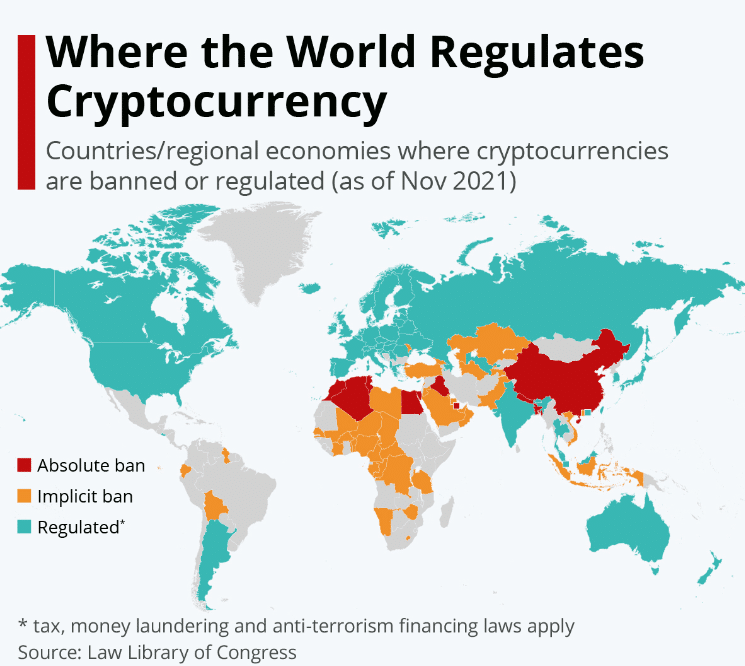

Source: Statista
China
- Legal status: Owning crypto is permitted; exchanges and ICOs are banned
- Tax rates: N/A
- Governing body: People’s Bank of China (PBOC)
China has a reputation for its strict laws, and crypto is no exception. However, contrary to common belief, there’s no outright ban on virtual currencies. Owning crypto isn’t illegal, but trading it on foreign exchanges or using it for payments? While no specific law prohibits these activities, the government makes them extremely difficult.
In 2013, the People’s Bank of China issued a Notice on Preventing Bitcoin Risks, clamping down heavily on crypto businesses, including exchanges, ICOs, new tokens, and other projects.
Furthermore, China sees crypto as a virtual commodity rather than a real currency.
So, while you won’t be prosecuted for owning crypto, there’s virtually no use for it in the region. China prioritizes control over its financial system and is concerned about digital currencies destabilizing it and enabling illicit activities.
Additionally, China is currently revising its AML laws to include virtual assets. This could potentially result in stricter regulations and penalties for using crypto.
Since China doesn’t recognize crypto, there are also no specific tax regulations. Instead of worrying about Bitcoin, China is busy developing its own central bank digital currency (CBDC), which will give the government greater control over citizens’ financial activities.
Think of it as the polar opposite of crypto – one’s all about decentralization, and the other’s about keeping a tight grip. It’s a safe bet that most would prefer the freedom of crypto, which is probably why the Chinese government is working overtime to tighten the reins.
Canada
- Legal status: Legal (treated as commodities)
- Tax rates: 15%–33% capital gains tax on profits
- Governing bodies: Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC), Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA)
Unlike many countries that have vague or non-existent crypto legislation, Canada has a proactive approach. It was the first country to approve a Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF) on the Toronto Stock Exchange.
This move shows Canada’s openness to innovation. Overall, the country opts for regulations over restrictions to mitigate risks without hampering progress.
While Canada allows the holding and trading of crypto, virtual money is not legal tender like the Canadian dollar.
The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) treats crypto trading as barter transactions, meaning you must report your gains on your tax return. The rate depends on your marginal tax bracket.
Furthermore, if you mine crypto, your profit is considered business income and is taxed accordingly. However, there is no tax on buying or holding crypto.
Crypto firms are classified as Money Service Businesses (MSBs), which brings them under the purview of the FINTRAC, Canada’s financial intelligence unit. FINTRAC employs AML laws like KYC and Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) procedures.


The Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA) is also actively involved in regulating crypto trading platforms. They determine if a crypto asset qualifies as a security and falls under respective laws.
United Kingdom
- Legal status: Legal (treated as unregulated financial instruments)
- Tax rates: 10%–20% capital gains tax on profits
- Governing body: Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
Similarly to Canada, the UK takes a proactive and balanced outlook on virtual currency regulations. Crypto businesses must play by the book and comply with KYC and AML procedures.
Here’s where things get interesting. Recently, the Financial Services and Markets Act 2022 (FSMA 2022) brought certain crypto assets under the FCA’s regulatory umbrella.
This means crypto trading now faces similar rules as traditional investments. Crypto businesses need to get a proper FCA license and implement consumer protection measures to ensure everyone plays fairly.
The FSMA might also pave the way for further regulations. By mid-2024, the UK government plans to introduce secondary legislation that outlines specific rules for crypto activities under FCA’s purview.
Stablecoins (cryptos pegged to traditional currencies) have caught the attention of UK authorities. Their perceived stability could lead to wider adoption, potentially impacting traditional financial systems as people flock to digital money.
Despite the name, stablecoins aren’t risk-free. The mechanism that maintains their value is complex and vulnerable to disruptions.
If a stablecoin loses its peg or experiences a significant price drop, it could cause wider financial instability.


That’s why the Financial Services and Markets Bill (FSMB) has been fast-tracked through Parliament’s Upper House. It aims to keep stablecoins in check.
Meanwhile, UK citizens must pay capital gains tax on their investment profits. Short-term and long-term capital gains fall under the same umbrella and are taxed at 10%-20%, depending on your early earnings.
Japan
- Legal status: Legal (treated as legal property)
- Tax rates: 15%–55% income tax
- Governing body: Financial Services Agency (FSA)
Japan is known for its progressive stance on technological innovation, whether humanoid robots, renewable energy, or blockchain. That’s why Japan recognized crypto as legal property and developed appropriate laws relatively early, in 2017.
The FSA regulates crypto exchanges in Japan, requiring them to register and comply with AML rules. Money laundering appears to be the government’s primary concern, with new laws trying to close any loopholes that malicious actors could exploit.
For instance, Japan introduced the ‘Travel Rule,’ which mandates exchanges share customer information when transferring crypto to other platforms. This law was first issued in 1995 with fiat currency in mind but was amended for crypto in 2023.
Applying an old law to a new technology wasn’t seamless.
Banks dealing with fiat money had to include information like transfer references and the sender’s legal name.
Crypto transactions include no data beyond the transfer amount and wallet address, so regulations are still underwork.
Unlike many countries that treat crypto as capital gains for tax purposes, Japan classifies it as miscellaneous income. This means you must pay the same tax as you would from freelance work or side hustle.
Japan has a progressive tax system, so the rate you pay depends on your overall income. Generally, it ranges from 15% to 55%, significantly higher than the capital gains tax rate of 20%.
On a good note, you don’t have to report crypto gains if they don’t exceed $1,5k a year.
Australia
- Legal status: Legal (treated as virtual assets)
- Tax rates: 12%–35% capital gains tax on profits
- Governing bodies: Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), Australian Taxation Office (ATO)
Australia didn’t reinvent the wheel with its crypto taxation regulations. The government treats crypto as capital gains, so you must pay 12%–35% tax depending on your overall yearly income.
However, if you earn under $13,5K a year, you can enjoy your crypto profits tax-free.
Furthermore, holding your crypto for over 12 months before selling it gives you a 50% capital gains discount. It seems the Australian government is all in for HODLing.


Crypto exchanges operating in Australia must comply with regulations set by the Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre (AUSTRAC). This includes KYC and AML procedures, which are the standard globally.
On the other hand, Australia threw a curveball with its ban on privacy coins. Tokens like Monero and Zcash make transactions difficult to trace, so the government is concerned about their use in money laundering. Most countries are still wrestling with how to handle privacy coins, and few have taken an equally bold step.
Singapore
- Legal status: Legal (treated as property)
- Tax rates: 0%–22% income tax
- Governing body: Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
Like the UK, Singapore treats cryptocurrency as property, not legal tender, so it could be subject to capital gains tax. However, Singapore doesn’t tax income from the sale of assets, contributing to its image of a ‘safe haven’ for crypto investors.
Here’s the catch. Despite the lack of capital gains tax, you may have to pay income tax if authorities deem them part of your core business activities.
They consider the frequency of trading, your investment amount, and the use of special infrastructure. Still, the tax rate ranges from 0% to 22%, which isn’t that bad compared to Japan.
Singapore also has AML and KYC laws for crypto businesses, like most countries we discussed above. Exchanges, DeFi platforms, and other firms must report to MAS under the Payment Services Act (PSA).
In 2022, MAS advised crypto businesses to limit mass advertising. Such cautiousness indicates Singapore is rolling out the red carpet for seasoned crypto players, not those just dipping their toes in the water.
South Korea
- Legal status: Legal; privacy coins and ICOs are banned
- Tax rates: 5%–45% miscellaneous income tax
- Governing bodies: Korea Financial Intelligence Unit (KFIU), self-regulatory organizations (SROs)
Like most countries, South Korea requires all crypto businesses to register with the KFIU and comply with AML and KYC laws.
However, South Korean exchanges also have self-regulatory organizations (SROs) established by the crypto industry itself. These SROs operate under the KFIU’s provision but can set additional rules for token listings, trading practices, and investor protection.
South Korea takes a zero-tolerance approach to crypto shenanigans. For example, they’ve banned Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) altogether due to the high risk of scams. Privacy coins also got the boot to combat money laundering and financial terrorism.
Profits from crypto trading are taxed at 5%–45% as miscellaneous income, depending on your total yearly earnings. But there’s more – authorities are discussing introducing a capital gains tax in addition to the income tax.
All in all, South Korea has some of the strictest crypto regulations worldwide, but it’s far from China’s or Egypt’s complete crackdown. The government is open to innovation in the space but adopts new trends with caution.
India
- Legal status: Unclear
- Tax rates: 30% miscellaneous income tax + 1% tax deducted at source (TDS)
- Governing body: Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
India’s crypto regulations are somewhat vague. Unlike some countries that have either embraced or outlawed digital currencies, India remains firmly on the fence.
Recently, the government proposed a bill banning unregulated virtual currencies. This could spell trouble for crypto investors, especially if India launches its own CDBC, a potential competitor to BTC and ETH.


Despite the unclear legal status, the Indian government isn’t shy about taking its cut.
They currently levy a hefty 30% tax on crypto profits, significantly higher than many other nations. To add insult to injury, they also impose a 1% TDS on crypto transactions over ₹50,000 (roughly $600).
With no clear-cut crypto laws, AML and KYC procedures also play a waiting game. It seems India’s current strategy is to keep an eye on the global crypto scene before making a decisive move.
Brazil
- Legal status: Legal payment method
- Tax rates: 5%–45% miscellaneous income tax
- Governing bodies: Securities and Exchange Commission of Brazil (CVM), Central Bank of Brazil (BACEN)
Contrary to India, Brazil is the frontrunner in crypto adoption. Cryptocurrencies are a legal payment method countrywide, so Brazilian businesses can accept BTC, ETH, and other approved tokens alongside cash and credit cards.
This is unsurprising given Brazil’s history of an inflationary rollercoaster that made its citizens wary of fiat currencies. Some Brazilians might see crypto as a more reliable way to store their hard-earned cash.
However, Brazil isn’t going all-in without any guardrails. The BCB requires all crypto service providers to register and comply with standard AML and KYC regulations.
Furthermore, depending on your total annual income, the tax on crypto trading profits can get hefty. There’s no capital gains tax, but you must pay a 5%–45% miscellaneous income tax rate.
El Salvador
- Legal status: Legal tender
- Tax rates: 0% capital gains tax on BTC
- Governing body: SSF
El Salvador made headlines when it became the first (and so far, only) country to make Bitcoin legal tender. Unlike Brazil, where businesses can choose to accept BTC or not, El Salvador flipped the switch to mandatory.


Following this bold move, the government distributed free crypto wallets to citizens through their state-sponsored app, Chivo (which, for all you Spanish enthusiasts, means ‘cool’). This decision aimed to get everyone on board the Bitcoin train.
What’s more, El Salvador offers tax benefits for foreigners investing in crypto. With exemptions from capital gains taxes, the country hopes to attract foreign cash and fuel economic growth.
However, there are still a few kinks to iron out. Regulations for crypto businesses are still underway. There are no specific AML or KYC requirements or consumer protections, which raises concerns about illegal crypto activities.
Another hurdle El Salvador faces is BTC’s inherent volatility, making it a gamble for everyday transactions. Finally, let’s not forget the digital divide.
Not everyone in El Salvador has access to smartphones or the internet, which are crucial for using the Chivo wallet. This creates a situation where some citizens are left out of the Bitcoin bonanza.
Switzerland
- Legal status: Legal (treated as movable assets)
- Tax rates: 0%–0.99% wealth tax, no capital gains tax
- Governing bodies: Swiss Federal Tax Administration (SFTA), Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA)
Similar to El Salvador and Brazil, Switzerland is pioneering crypto adoption. In 2020, it introduced laws concerning the notion of distributed ledger technology (DLT) securities. In essence, Switzerland created a legal framework that welcomes innovation within the crypto industry.
But let’s talk specifics. How is crypto taxed in Switzerland? Well, it depends on your tax status and how you use your crypto. For individual investors, things can be quite budget-friendly.
Switzerland treats crypto as movable assets and applies wealth tax at the cantonal level (think state level). These rates are capped at a chill 0.99% of your total assets.
The SFTA maintains a list with tax values for common cryptos to simplify the process.
Here’s the real kicker: there’s no capital gains tax on your crypto profits.
However, the capital gains tax exception only applies to private investors, not professional traders or businesses.
Furthermore, Switzerland operates a tiered licensing system for crypto businesses. For lower-risk activities like custody (holding crypto for clients) or basic trading platforms, a simpler ‘Finma Innovation License’ may suffice.
However, if you’re running a full-fledged crypto exchange, you’ll need a more comprehensive license from FINMA.
Of course, AML and KYC regulations are very much in play for crypto businesses in Switzerland. The Swiss government also recognizes the importance of educating consumers – for example, FINMA has a dedicated blog.
European Union
- Legal status: Legal (may vary by country)
- Tax rates: Varies by country
- Governing body: European Parliament
The EU leaves much of the responsibility for crypto rules to individual member countries, so it feels like a regulatory patchwork.
Taxation is a prime example of this diversity. Portugal welcomes crypto gains with open arms, treating them like tax-free income (under certain conditions).
Head north to Denmark, however, and you might face a whopping tax rate that could make your eyes water (up to 52.07%).
Cyprus, Estonia, Malta, and Slovenia residents enjoy a 0% capital tax on their crypto investments, whereas Finland, Germany, and Sweden impose some of the highest taxes, over 30%. Most countries, however, charge up to 20% tax.
It’s not all doom and gloom for high-rolling crypto enthusiasts, though. Countries like Cyprus, Estonia, Malta, and Slovenia have a 0% capital gains tax.
This stands in stark contrast to Finland, Germany, and Sweden, where tax rates can climb past 30%. Most EU countries fall somewhere in the middle, levying a tax rate of up to 20% on crypto profits.


Despite the tax chaos, the EU is making strides towards a more unified approach to crypto regulation.
The Fifth and Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directives (5AMLD and 6AMLD) are now in place across the bloc. They require cryptocurrency service providers to adhere to KYC and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) regulations.
In April 2023, the European Parliament took another step towards harmonization. They now require crypto service providers, such as exchanges and custodians, to obtain an operational license.
If you live in the EU, it’s important to do your due diligence on your local tax, reporting, and registration implications before diving headfirst into trading.

What are the Downsides to Regulating Digital Assets
We’ve briefly touched on the benefits of crypto regulations. However, excessive government control also has downsides. Let’s discuss some of them.
Stifling innovation
Blockchain technology is still evolving, and strict laws could dampen innovation. Do we want a world where groundbreaking ideas are shelved because they don’t tick all the regulatory boxes?
Market entry hurdles
Regulations often throw up roadblocks like licensing requirements and mountains of paperwork. These barriers prevent new startups from entering the market, hindering healthy competition.
Individual investors may also suffer. For example, the US SEC is considering regulations limiting participation in certain ICOs to accredited investors. These are typically individuals with a high income or a net worth of over $1 million.
Excessive regulations can limit the investment opportunities available to the general public and potentially concentrate wealth in the hands of a select few.
Enforcement challenges
Crypto transactions are borderless. However, there’s no global consensus on how to regulate them, so it’s hard to understand which rules apply to specific cases. For instance, a crypto exchange operating in one country might be subject to stricter KYC procedures than in another.
Operational overheads
The crypto space might be virtual, but the bills are very real. Businesses might have to shell out for specialized software and compliance specialists, which translates into higher fees for customers.
Smaller crypto companies might get squeezed out entirely, unable to afford the ever-growing compliance burden.
Market volatility
Sudden changes in regulations can send the crypto market on a wild ride. To illustrate, if people are unsure how new rules will impact their investments, they might panic sell, leading to sudden price drops.
Investor outflow
Ultimately, any government’s primary goal is to balance restrictions with investor support. After all, they want to collect as much tax revenue as possible while fighting illegal activities and keeping an eye on citizens’ transactions.
If cryptocurrency regulations are too strict, investors might flee to a country with a more lenient approach. This may hinder the country’s technological development and leave it behind the global curve.
Final Thoughts
The spectrum of global crypto regulations is broad. While some governments fully legalize crypto and incentivize investors with low tax rates, like El Salvador, others remain wary or ban crypto altogether.
Remember, the regulations are a work in flux. Before you plunge into trading, it’s crucial to Do Your Own Research (DYOR) about your local laws.
FAQs
Is there any regulation on cryptocurrency?
Yes, but each country has its own crypto regulations. Some countries have strict KYC, AML, and consumer protection rules, while others have almost none. It’s important to research crypto payment regulations in your region before diving into crypto. Read more under ‘What Does Regulation for Cryptocurrency Mean?’.
What is the new regulation for crypto?
New crypto regulations appear all the time. For example, the UK government plans to introduce secondary legislation that outlines specific rules for crypto activities by mid-2024. Likewise, many other countries are working on legislation or updating existing frameworks to address cryptocurrencies.
Should the SEC regulate crypto?
The SEC focuses on securities rather than all cryptocurrencies. Securities are crypto investments made to raise capital. Usually, investors don’t actively manage the asset. Therefore, cryptocurrencies that function as a medium of exchange or utility tokens don’t count as securities. Read more under ‘How is Crypto Regulated in the United States?’.
What regulatory protections currently apply to crypto assets?
Regulatory protections vary by country. For example, many countries have AML and KYC procedures in place. Some mandate crypto project disclosures and provide educational resources to investors. Read more under ‘Rules and Regulations for Cryptocurrency Around the World.’
References

 Our Editorial Process
Our Editorial Process
The Tech Report editorial policy is centered on providing helpful, accurate content that offers real value to our readers. We only work with experienced writers who have specific knowledge in the topics they cover, including latest developments in technology, online privacy, cryptocurrencies, software, and more. Our editorial policy ensures that each topic is researched and curated by our in-house editors. We maintain rigorous journalistic standards, and every article is 100% written by real authors.
Regulation
Cryptocurrency Regulation in Slovenia 2024

Slovenia, a small but highly developed European country with a population of 2.1 million, boasts a rich industrial history that has contributed significantly to its robust economy. As the most economically developed Slavic nation, Slovenia has grown steadily since adopting the euro in 2007. Its openness to innovation has been a key factor in its success in the industrial sector, making it a favorite destination for cryptocurrency enthusiasts. Many believe that Slovenia is poised to become a powerful fintech hub in Europe. But does its current cryptocurrency regulatory framework support such aspirations?
Let’s explore Slovenia’s cryptocurrency regulations and see if they can push the country to the forefront of the cryptocurrency scene. My expectations are positive. What are yours? Before we answer, let’s dig deeper.
1. Cryptocurrency Regulation in Slovenia: An Overview
Slovenia is known for its pro-innovation stance, providing a supportive environment for emerging technologies such as blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Under the Payment Services and Systems Act, cryptocurrencies are classified as virtual assets rather than financial or monetary instruments.
Regulation of the cryptocurrency sector in Slovenia is decentralized. Different authorities manage different aspects of the ecosystem. For example, the Bank of Slovenia and the Securities Market Agency supervise cryptocurrency transactions to ensure compliance with financial laws, including anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing regulations. The Slovenian Act on the Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing (ZPPDFT-2) incorporates the EU’s Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (5MLD) and aligns with the latest FATF recommendations. All virtual currency service providers must register with the Office of the Republic of Slovenia.
2. Cryptocurrency regulation in Slovenia: what’s new?
This year, there have been several noteworthy developments in the cryptocurrency sector in Slovenia:
July 25, 2024: Slovenia has issued a €30 million on-chain sovereign digital bond, the first of its kind in the EU, with a yield of 3.65%, maturing on 25 November 2024.
May 14, 2024: NiceHash has announced the first Slovenian Bitcoin-focused conference, NiceHashX, scheduled for November 8-9 in Maribor.
3. Explanation of the legal framework for cryptocurrency taxation in Slovenia
Slovenia’s cryptocurrency tax framework provides clear guidelines for both individuals and businesses. According to the Slovenian Tax Administration, tax treatment depends on the status of the trader and the nature of the transaction.
- Individuals: Income earned from cryptocurrencies through employment or ongoing business activities is subject to personal income tax. However, capital gains from trading or market fluctuations are exempt from taxation.
- Society: Capital gains from cryptocurrency activities are subject to a corporate income tax of 19%. Value added tax (VAT) generally applies at a rate of 22%, although cryptocurrency transactions considered as means of payment are exempt from VAT. Companies are not allowed to limit payment methods to cryptocurrencies only. Tokens issued during ICOs must comply with standard accounting rules and the Corporate Tax Act.
4. Cryptocurrency Mining in Slovenia: What You Should Know
Cryptocurrency mining is not restricted in Slovenia, but the income from mining is considered business income and is therefore taxable. This includes rewards from validating transactions and any additional income from mining operations. Both natural persons and legal entities must comply with Slovenian tax regulations.
5. Timeline of the evolution of cryptocurrency regulations in Slovenia
Here is a timeline highlighting the evolution of cryptocurrency regulations in Slovenia:
- 2013:The Slovenian Tax Administration has issued guidelines according to which income from cryptocurrency transactions should be taxed.
- 2017:The Slovenian Tax Administration has provided more detailed guidelines on cryptocurrency taxation, based on factors such as the trader’s status and the type of transaction.
- 2023The EU has adopted the Markets in Cryptocurrencies Regulation (MiCA), which establishes a uniform regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies, their issuers and service providers across the EU.
Final note
Slovenia’s approach to the cryptocurrency industry is commendable, reflecting its optimistic view of the future of cryptocurrency. The country’s balanced regulatory framework supports cryptocurrency innovation while protecting user rights and preventing illegal activities. Recent developments demonstrate Slovenia’s commitment to continuously improving its regulatory environment. Slovenia’s cryptocurrency regulatory framework sets a positive example for other nations navigating the evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
Read also: Cryptocurrency Regulation in Hong Kong 2024
Regulation
A Blank Slate for Cryptocurrencies: Kamala Harris’ Regulatory Opportunity

Photo by The Dhage of Shubham ON Disinfect
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, the need for clear regulation has never been greater.
Vice President Kamala Harris is now leading the charge on digital asset regulation in the United States, presenting a unique opportunity for a clean slate. This fresh start can foster innovation and protect consumers. It can also pave the way for widespread adoption across industries, including real estate agencies, healthcare providers, and online gambling platforms like these online casinos in the uk. According to experts at SafestCasinoSites, these platforms have advantages such as bonus offers, a wide selection of games, and various payment methods. Ultimately, all this increased adoption could push the cryptocurrency market forward.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at the current state of cryptocurrency regulation in the United States, which is a complex and confusing landscape. Multiple agencies, including the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), have overlapping jurisdictions, creating a fragmented regulatory environment. This lack of clarity has hindered innovation, as companies are reluctant to invest in the United States, fearing regulatory repercussions. A cohesive and clear regulatory framework is urgently needed to unlock the full potential of cryptocurrencies in the United States.
While the US struggles to find its footing, other countries, such as Singapore and the UK, are actively embracing the cryptocurrency industry with clear and supportive regulatory frameworks. This has led to a brain drain, with companies opting to set up in more hospitable environments.
Vice President Kamala Harris has a unique opportunity to change this narrative and clean up the future. cryptocurrency regulation. By taking a comprehensive and inclusive approach, it can help create a framework that balances consumer protection with innovation and growth. The time has come for clear and effective regulation of cryptocurrencies in the United States.
Effective regulation of digital assets is essential to fostering a safe and innovative environment. Key principles guiding this regulation include clarity, innovation, global cooperation, consumer protection, and flexibility. Clear definitions and guidelines eliminate ambiguity, while encouraging experimentation and development to ensure progress. Collaboration with international partners establishes consistent standards, preventing regulatory arbitrage. Strong safeguards protect consumers from fraud and market abuse, and adaptability allows for evolution in response to emerging trends and technologies, striking a balance between innovation and protection.
The benefits of effective cryptocurrency regulation are many and far-reaching. By establishing clear guidelines, governments can attract investors and traditional users, spurring growth and adoption. This, in turn, can position countries like the United States as global leaders in financial technology and innovation. Strong protections will also increase consumer confidence in digital assets and related products, boosting economic activity.
A thriving cryptocurrency industry can significantly contribute to GDP and job creation, which has a positive impact on the overall economy. Furthermore, effective regulation has paved the way for the growth of many companies such as tech startups, online casinos, and pharmaceutical companies, proving that clear guidelines can unlock new opportunities without stifling innovation. This is a great example of how regulation can alleviate fears of regressive policies, even if Kamala Harris does not repeal the current progressive approach. By adopting effective regulation, governments can create fertile ground for the cryptocurrency industry to thrive, driving progress and prosperity.
Regulation
Think You Own Your Crypto? New UK Law Would Ensure It – DL News

- The UK Law Commission has developed a bill that will address a situation of legal uncertainty.
- The commission’s goal is to ensure that cryptocurrencies are legally treated as personal property.
UK law is not entirely clear whether cryptocurrencies can be considered personal property.
This is according to the UK Law Commission, which argues that while most investors assume that when they buy cryptocurrencies, they are “acquiring property rights in the same way as buying, say, a watch or a laptop.”
“As the law currently stands, this is not necessarily the case,” the respected legal body said in a new report on Tuesday.
The report was accompanied by a solution: a new bill to consolidate the legal status of digital assets as personal property.
This could be huge for the estimated 4.7 million Britons valued hold cryptocurrencies.
“This will allow the courts to determine a range of issues,” the report says.
If passed, the law would help clarify how cryptocurrencies are treated in cases of bankruptcy, estate planning or theft.
Flexible law
The commission is an independent body responsible for reviewing UK law. It began investigating whether English and Welsh property laws apply to digital assets in 2020.
Join the community to receive our latest stories and updates
At the time, then-Chancellor of the Exchequer Rishi Sunak expressed ambitions to transform the UK into a cryptocurrency hub as Britons invested more.
In 2023, the commission decided that, in most cases, the legislation of England and Wales is sufficiently flexible to regulate cryptocurrencies.
This means that any asset, from Bitcoin to non-fungible tokens and some types of digital contracts, can be considered personal property, without Parliament having to write extensive new laws.
There was one small area of uncertainty, however: it was unclear whether cryptocurrencies fell within the two categories of personal property recognised under UK law.
These two categories are made up of tangible assets (cars, laptops, bags) and intangible assets (contracts, stocks, and debt).
The bill that will now go to Parliament to be converted into law aims to remedy this situation.
Without that clarification, courts may try to lump cryptocurrencies together with intangible assets, said Adam Sanitt, head of litigation, knowledge, innovation and corporate support EMEA at law firm Norton Rose Fulbright. DL News in March.
This is problematic because intangible assets are creations of the legal system, while cryptocurrencies are not.
“How the law treats digital assets, what rights you have over them, how you own them, how you transfer them to other people—that treatment is different, because digital assets don’t exist by virtue of the legal system, but independently of it,” Sanitt said.
The money in your bank account, for example, is a legal creation. The government could pass a law to cancel it.
However, if the UK passed a law banning Bitcoin, Bitcoin would not cease to exist.
Sanitt said: “That’s why digital assets are so important: neither the government nor the legal system can take them away from you.”
Contact the author at joanna@dlnews.com.
Regulation
The Solution the Cryptocurrency Industry Needs

The cryptocurrency industry has performed remarkably well since its inception, but now faces a critical hurdle that requires careful consideration and regulatory expertise to overcome. Despite the industry’s rapid growth and rate of global adoption, the gap between the industry and global regulation is only widening as new innovations break through into the public domain.
Although efforts are being made on both sides, regulators’ lack of familiarity with cryptocurrencies and the industry’s lack of regulatory expertise are hindering innovation in the sector. To address this issue, traditional financial institutions (TradFi) such as MultiBank Group have started venturing into the cryptocurrency sector.
The regulatory gap
Over the past decade, the cryptocurrency industry has grown dramatically as tech entrepreneurs and forward-thinking thinkers have founded a plethora of crypto platforms and protocols to push the boundaries of the space. The problem faced by these newcomers, who are often unfamiliar with the hurdles posed by financial regulators, can quickly overwhelm and stall operations.
On the other hand, regulators more attuned to TradFi systems may be equally stifled by the complexities of decentralization and blockchain technology. The unfamiliarity experienced by both innovators and regulators creates a stark regulatory divide between both sides, leading to misunderstandings and potential conflicts.
To overcome this lack of communication, a bridge must be built to bridge the gap, ensuring future stability for the cryptocurrency industry and clearer legislation from regulators.
Efforts to bridge the gap between industry
The gap between the cryptocurrency industry and regulators is slowly narrowing as efforts to regulate cryptocurrencies and Web3 space activities are gaining momentum. Specific regulatory actions are taking place in many countries, aimed at providing greater oversight of cryptocurrency transactions, cryptocurrency exchanges, and initial coin offerings (ICOs).
Despite being a positive step in the right direction, these new regulations can differ significantly between jurisdictions around the world. This fragmentation results in a regulatory environment filled with obstacles, bottlenecks, and varying requirements and prohibitions. As cryptocurrency companies and TradFi institutions attempt to navigate the minefield, the regulatory maze becomes increasingly convoluted.
TradFi institutions like MultiBank Group are working to solve this problem, as one of the largest financial derivatives institutions in the world with over 12 licenses across all continents. Founded in 2005, the Group has an impeccable and trustworthy reputation globally, extensive expertise in financial regulation and has now ventured into the cryptocurrency space via MultiBank.io.
MultiBank.io: TradFi Excellence in the Crypto Space
Expanding into the cryptocurrency space via MultiBank.io has enabled MultiBank Group to provide regulatory clarity and trust to the digital asset industry. With a substantial daily trading volume of $12.1 billion, the timely decision to enter the cryptocurrency space has the potential to set regulatory precedents and standards for years to come.
By helping to develop sensible and well-considered regulations, MultiBank.io’s established reputation allows the company to communicate effectively and clearly with regulators. Unlike others in the industry without regulatory expertise, MultiBank.io facilitates the Group’s commitment to rigorous regulatory standards, the scope of oversight and establishes the necessary transparency.
The company’s approach ensures that regulatory licenses are pre-acquired, compliance is met globally without jurisdictional barriers, and transactions remain secure at all times. By helping to create robust regulations that are both clear and innovation-friendly, MultiBank Group looks forward to standardizing the entire cryptocurrency industry for other potential innovators.
One of the biggest challenges in establishing a clearly constructed bridge between regulators and the cryptocurrency industry is effective communication. By leveraging its institutional background TradFi and acting as an intermediary with regulators, MultiBank Group is able to translate the needs of the industry to those who shape it.
This quality of mediation is essential to ensure that regulation helps develop essential technological advances rather than hinders their establishment and growth. Through the lens of TradFi when looking at the complexity of the cryptocurrency industry, MultiBank Group is able to deconstruct unfamiliar crypto arguments for regulation and create a safer and more secure space.
Where TradFi and Crypto Meet
Regulations are crucial for traders, investors, and everyday users of crypto platforms and their safety when participating in crypto markets. While strict regulations are necessary for stable market integrity, innovation should still be considered, something MultiBank Group considers a priority.
Where TradFi and cryptocurrencies converge, the Group is there to provide a balanced approach to ensure promotion for both the cryptocurrency industry and regulators seeking to protect both retail and institutional investors. This balance is critical to maintaining a thriving space where cryptocurrency innovation can thrive without compromising the security of user funds or data.
As more TradFi institutions like MultiBank Group enter the cryptocurrency space with ever-expanding expertise in regulatory understanding, the future of the industry is increasingly encouraged. The financial freedoms of the cryptocurrency space coupled with regulatory oversight for financial security will be the guiding lights for the future success of the entire cryptocurrency industry.
No spam, no lies, just insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
-
 Ethereum12 months ago
Ethereum12 months agoEthereum Posts First Consecutive Monthly Losses Since August 2023 on New ETFs
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoCryptocurrency Regulation in Slovenia 2024
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoNew bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoThink You Own Your Crypto? New UK Law Would Ensure It – DL News
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoUpbit, Coinone, Bithumb Face New Fees Under South Korea’s Cryptocurrency Law
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoA Blank Slate for Cryptocurrencies: Kamala Harris’ Regulatory Opportunity
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoBahamas Passes Cryptocurrency Bill Designed to Prevent FTX, Terra Disasters
-

 Regulation12 months ago
Regulation12 months agoIndia to Follow G20 Policy for Cryptocurrency Regulation: MoS Finance
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago“Captain Tsubasa – RIVALS” launches on Oasys Blockchain
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 News12 months ago
News12 months agoEU supports 15 startups to fight online disinformation with blockchain
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto





