News
Cos’è Bitcoin? Come funziona? – Consigliere di Forbes

Nota editoriale: guadagniamo una commissione dai collegamenti dei partner su Forbes Advisor. Le commissioni non influenzano le opinioni o le valutazioni dei nostri redattori.
Non solo Bitcoin (BTC) è la prima criptovaluta, ma è anche la più conosciuta tra le oltre 19.000 criptovalute esistenti oggi. I media finanziari coprono con entusiasmo ogni nuovo drammatico picco e declino da rivoltare lo stomaco, rendendo Bitcoin una parte inevitabile del panorama.
Anche se la volatilità selvaggia potrebbe produrre grandi titoli sui giornali, difficilmente rende Bitcoin la scelta migliore per gli investitori alle prime armi o per le persone che cercano una riserva di valore stabile. Comprendere i dettagli può essere complicato: diamo un’occhiata più da vicino a come funziona Bitcoin.
Offerte dei partner in primo piano
Commissioni di negoziazione
Commissione Maker 0,4% / Commissione Taker 0,6%.
Cos’è Bitcoin?
Bitcoin è una valuta digitale decentralizzata che puoi acquistare, vendere e scambiare direttamente, senza intermediari come una banca. Il creatore di Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamotooriginariamente descriveva la necessità di “un sistema di pagamento elettronico basato sulla prova crittografica invece che sulla fiducia”.
Ogni transazione Bitcoin mai effettuata esiste su un registro pubblico accessibile a tutti, rendendo le transazioni difficili da annullare e difficili da falsificare. Questo è previsto: al centro della loro natura decentralizzata, i Bitcoin non sono supportati dal governo o da qualsiasi istituzione emittente, e non c’è nulla che ne garantisca il valore oltre alle prove inserite nel cuore del sistema.
“Il motivo per cui vale denaro è semplicemente che noi, come persone, abbiamo deciso che ha valore, come l’oro”, afferma Anton Mozgovoy, co-fondatore e CEO della società di servizi finanziari digitali Holyheld.
Dal suo lancio pubblico nel 2009, il valore del Bitcoin è aumentato notevolmente. Anche se una volta veniva venduto per meno di 150 dollari a moneta, all’8 giugno 1 BTC equivale a circa 30.200 dollari. Poiché la sua offerta è limitata a 21 milioni di monete, molti si aspettano che il suo prezzo continui a salire col passare del tempo, soprattutto perché gli investitori istituzionali più grandi iniziano a trattarlo come una sorta di oro digitale per proteggersi dal mercato. volatilità E inflazione. Attualmente ci sono più di 19 milioni di monete in circolazione.
I migliori scambi di criptovalute del 2024
Abbiamo esaminato le principali offerte di scambio e le risme di dati per determinare i migliori scambi di criptovalute.
Come funziona Bitcoin?
Bitcoin è costruito su un record digitale distribuito chiamato a blockchain. Come suggerisce il nome, la blockchain è un insieme di dati collegati, composto da unità chiamate blocchi contenenti informazioni su ogni transazione, tra cui data e ora, valore totale, acquirente e venditore e un codice identificativo univoco per ogni scambio. Le voci vengono messe insieme in ordine cronologico, creando una catena digitale di blocchi.
“Una volta che un blocco viene aggiunto alla blockchain, diventa accessibile a chiunque desideri visualizzarlo, fungendo da registro pubblico delle transazioni di criptovaluta”, afferma Stacey Harris, consulente di Pelicoin, una rete di criptovaluta ATM.
La blockchain è decentralizzata, il che significa che non è controllata da nessuna organizzazione. “È come un documento Google su cui chiunque può lavorare”, afferma Buchi Okoro, CEO e cofondatore dell’exchange di criptovalute africano Quidax. “Nessuno lo possiede, ma chiunque abbia un collegamento può contribuire ad esso. E man mano che persone diverse lo aggiornano, anche la tua copia viene aggiornata.
Sebbene l’idea che chiunque possa modificare la blockchain possa sembrare rischiosa, in realtà è ciò che rende Bitcoin affidabile e sicuro. Affinché un blocco di transazione possa essere aggiunto alla blockchain di Bitcoin, deve essere verificato dalla maggior parte di tutti i possessori di Bitcoin e i codici univoci utilizzati per riconoscere i portafogli e le transazioni degli utenti devono essere conformi al giusto modello di crittografia.
Questi codici sono numeri lunghi e casuali, il che li rende incredibilmente difficili da produrre in modo fraudolento. Il livello di casualità statistica nei codici di verifica blockchain, necessari per ogni transazione, riduce notevolmente il rischio che qualcuno possa effettuare transazioni Bitcoin fraudolente.
Come funziona il mining di Bitcoin?
Il mining di Bitcoin è il processo di aggiunta di nuove transazioni alla blockchain di Bitcoin. È un lavoro duro. Le persone che scelgono di estrarre Bitcoin utilizzano prove di lavoro, utilizzando computer in una gara per risolvere enigmi matematici che verificano le transazioni.
Per invogliare i minatori a continuare a correre per risolvere gli enigmi e supportare il sistema generale, il codice Bitcoin premia i minatori con 6,25 BTC per ogni nuovo blocco. Tale importo di BTC equivale a quasi $ 190.000.
“Ecco come vengono create le nuove monete” e le transazioni recenti vengono aggiunte alla blockchain, afferma Okoro.
All’inizio era possibile per la persona media estrarre Bitcoin, ma non è più così. Il codice Bitcoin è scritto per rendere la risoluzione dei suoi enigmi sempre più impegnativa nel tempo, richiedendo sempre più risorse informatiche. Oggi, per avere successo, il mining di Bitcoin richiede computer potenti e l’accesso a enormi quantità di elettricità a basso costo.
Inoltre, il mining di Bitcoin paga meno rispetto al passato, rendendo ancora più difficile recuperare i crescenti costi computazionali ed elettrici.
“Nel 2009, quando questa tecnologia è apparsa per la prima volta, ogni volta che ricevevi un francobollo, ricevevi una quantità di Bitcoin molto maggiore di quella che ottieni oggi”, afferma Flori Marquez, co-fondatore di BlockFi, una società di gestione patrimoniale crittografica. “Ci sono sempre più transazioni [now, so] l’importo che ti viene pagato per ogni francobollo è sempre meno.” Si stima che entro il 2140 tutti i Bitcoin saranno entrati in circolazione, il che significa che il mining non rilascerà nuove monete e i minatori potrebbero invece dover fare affidamento sulle commissioni di transazione.
Come utilizzare Bitcoin
Negli Stati Uniti, le persone generalmente utilizzano Bitcoin come investimento alternativo, aiutando a diversificare un portafoglio azioni E obbligazioni. Puoi anche utilizzare Bitcoin per effettuare acquisti, ma ci sono alcuni venditori che accettano la criptovaluta originale.
Le grandi aziende che accettano Bitcoin includono Microsoft, PayPal e Whole Foods, solo per citarne alcune. Potresti anche scoprire che alcuni piccoli rivenditori locali o alcuni siti web accettano Bitcoin, ma dovrai scavare un po’.
Puoi anche utilizzare un servizio che ti consente di connettere una carta di debito al tuo account crittografico, il che significa che puoi utilizzare Bitcoin nello stesso modo in cui utilizzeresti una carta di credito. Ciò implica generalmente anche che un fornitore finanziario converta istantaneamente i tuoi Bitcoin in dollari.
In altri paesi, in particolare quelli con valute meno stabili, le persone a volte usano la criptovaluta invece della propria valuta.
Bitcoin offre alle persone l’opportunità di immagazzinare valore senza fare affidamento su una valuta sostenuta da un governo. Offre alle persone la possibilità di proteggersi dallo scenario peggiore. Stai già vedendo persone in paesi come Venezuela, Argentina e Zimbabwe (paesi fortemente indebitati) dove Bitcoin sta ottenendo un’enorme popolarità.
Quando usi Bitcoin come valuta, non come investimento, negli Stati Uniti, devi essere consapevole di alcune cose implicazioni fiscali.
Come acquistare Bitcoin
La maggior parte delle persone acquista Bitcoin tramite scambi di criptovaluta. Gli scambi ti consentono di acquistare, vendere e detenere criptovaluta. La creazione di un account è simile all’apertura di un conto di intermediazione— dovrai verificare la tua identità e fornire una fonte di finanziamento, come un conto bancario o una carta di debito.
I principali scambi includono CoinBase, KrakenE Gemelli. Puoi anche acquistare Bitcoin presso un broker online come Robinhood.
Indipendentemente da dove acquisti il tuo Bitcoin, avrai bisogno di un Portafoglio Bitcoin in cui conservarlo. Questo potrebbe essere chiamato “portafoglio caldo” o “portafoglio freddo”.
Un hot wallet (chiamato anche portafoglio online) è conservato da un exchange o da un provider nel cloud. I fornitori di portafogli online includono Exodus, Electrum e Mycelium. Un portafoglio freddo (o portafoglio mobile) è un dispositivo offline utilizzato per archiviare Bitcoin e non è connesso a Internet. Alcune opzioni di portafoglio mobile includono Trezor e Ledger.
Alcune note importanti sull’acquisto di Bitcoin: sebbene Bitcoin sia costoso, puoi acquistarlo frazionario Bitcoin da alcuni fornitori. Dovrai anche prestare attenzione alle commissioni, che generalmente sono piccole percentuali dell’importo della transazione crittografica, ma possono sommarsi per acquisti di piccoli dollari. Infine, gli acquisti di Bitcoin non sono istantanei come molti altri acquisti di azioni. Poiché i minatori devono verificare le transazioni Bitcoin, potrebbero essere necessari almeno 10-20 minuti per vedere il tuo acquisto Bitcoin nel tuo account.
Come investire in Bitcoin
Come un’azione, puoi acquistare e detenere Bitcoin come un investimento. Puoi farlo anche adesso in conti pensionistici speciali chiamati IRA Bitcoin.
Non importa dove scegli di tenere il tuo Bitcoin, le filosofie delle persone su come investirlo variano: alcuni acquistano e mantengono a lungo termine, alcuni acquistano e mirano a vendere dopo un rialzo dei prezzi, e altri scommettono sulla diminuzione del prezzo. Il prezzo del Bitcoin nel corso del tempo ha subito grandi oscillazioni, scendendo da un minimo di 5.165 dollari ad un massimo di 28.990 dollari nel solo 2020.
“Penso che in alcuni luoghi le persone potrebbero usare Bitcoin per pagare qualcosa, ma la verità è che si tratta di un asset che sembra destinato ad aumentare di valore in tempi relativamente brevi per un po’ di tempo”, afferma Marquez. “Allora perché dovresti vendere qualcosa che varrà molto di più l’anno prossimo rispetto a oggi? La maggior parte delle persone che lo detengono sono investitori a lungo termine”.
I consumatori possono anche investire in un fondo comune Bitcoin acquistando azioni del Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC). Tuttavia, il requisito di investimento minimo è di $ 50.000. Ciò significa che la maggioranza degli americani non è in grado di crederci. In Canada, tuttavia, gli investimenti diversificati in Bitcoin stanno diventando più accessibili. Nel febbraio 2021, Purpose Bitcoin ETF (BTCC) ha iniziato a essere scambiato come il primo Bitcoin ETF al mondo e la Ontario Securities Commission ha anche approvato l’Evolve Bitcoin ETF (EBIT). Gli investitori americani che cercano Bitcoin o un’esposizione simile a Bitcoin possono prendere in considerazione gli ETF blockchain che investono nella tecnologia delle criptovalute.
Una nota importante: sebbene i fondi basati su criptovalute possano aggiungere diversificazione alle partecipazioni in criptovalute e diminuire leggermente il rischio, comportano comunque un rischio sostanzialmente maggiore e addebitano commissioni molto più elevate rispetto ai fondi su larga scala. fondi indicizzati con storie di rendimenti costanti. Gli investitori che desiderano aumentare costantemente la ricchezza possono optare per mutui e mutui basati su indici fondi negoziati in borsa (ETF).
Dovresti comprare Bitcoin?
Molti esperti finanziari supportano il desiderio dei loro clienti di acquistare criptovaluta, ma non lo consigliano a meno che i clienti non esprimano interesse. “La preoccupazione più grande per noi è se qualcuno vuole investire in criptovalute e l’investimento che sceglie non va bene, e poi all’improvviso non può mandare i propri figli al college”, afferma Ian Harvey, un pianificatore finanziario certificato (PCP) a New York. “Allora non valeva la pena rischiare.”
La natura speculativa della criptovaluta porta alcuni pianificatori a consigliarla per gli investimenti “laterali” dei clienti. “Alcuni lo chiamano conto Las Vegas”, afferma Scott Hammel, un CFP a Dallas. “Teniamolo lontano dalla nostra reale prospettiva a lungo termine. Assicurati che non diventi una parte troppo grande del tuo portafoglio.
Bitcoin è come un singolo titolo e i consulenti non consigliano di investire una parte considerevole del tuo portafoglio in una sola società. Al massimo, i pianificatori suggeriscono di investire non più dell’1%-10% in Bitcoin se ne sei appassionato. “Se fosse un titolo, non gli assegneresti mai una parte significativa del tuo portafoglio”, afferma Hammel.
News
Blockchain Technology Will Transform Water Access and Management Globally

Disclosure: The views and opinions expressed here are solely those of the author and do not represent the views and opinions of the crypto.news editorial team.
Access to clean water is a basic human need, yet billions of people around the world still struggle to get it. According to the World Health Organization, over 2 billion people live in countries suffering from severe water stress, and this number is expected to continue to grow due to climate change and population growth.
Traditional water management systems have struggled to address these challenges, often hampered by inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and misallocation of resources. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to these challenges, providing equitable access and sustainable use of this crucial resource.
The current state of water management
Water management today faces several pressing issues. Inefficiencies in water supply, distribution, and use, coupled with a lack of real-time monitoring, often result in resource waste and misallocation. Many water sources fail to realize their full potential due to infrastructure and financing shortfalls. For example, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) report indicated that the United States would need to invest $625 billion over the next 20 years to repair, maintain and improve the country’s drinking water infrastructure due to aging pipes and other infrastructure problems. Additionally, in the United States alone, household leaks can to waste nearly 900 billion gallons of water per year nationwide. This is equivalent to the annual domestic water consumption of nearly 11 million homes.
Furthermore, corruption and mismanagement of water resources can cause unequal distribution, with disadvantaged communities often bearing the brunt of water scarcity. For example, South Africa is struggling with myriad challenges to its water security: drought, inadequate water conservation measures, outdated infrastructure, and unequal access to water resources. The country faces significant water scarcity, with demand expected to outstrip supply by 2030, creating a projected gap of 17%.
Furthermore, the global water industry is highly monopolized, with a few key players controlling a significant share of the market. These companies exert substantial influence over the water supply chain, often prioritizing profit over equitable distribution and environmental responsibility. This concentration of power can lead to inflated prices and limited access for vulnerable populations. The global bottled water market alone is projected to reach $509.18 billion by 2030, with these large companies capturing a significant share of revenue. This monopolization exacerbates existing inequalities in water access and highlights the need for more decentralized and community-driven water management solutions.
Source: Grand View Search
The potential of blockchain in water management
Blockchain technology can address these issues by providing a transparent, secure, and decentralized platform for water resource management. This approach offers several advantages:
- Transparency and accountability. Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that all transactions and data entries are transparent and cannot be changed once recorded. This transparency can reduce corruption and ensure that water resources are allocated fairly and efficiently. For example, blockchain can be used to track water usage from source to end user, providing a clear record of how water is distributed and used. This level of transparency can help hold authorities accountable and manage water resources sustainably.
- Efficient resource management. Blockchain can facilitate the creation of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into the code. These contracts can automate water distribution based on real-time data, directing water to where it is needed most. For example, smart contracts could be used to manage urban water supply systems, automatically adjusting water distribution based on real-time consumption patterns and demand. This can help optimize water use, reduce waste, and ensure that households and businesses receive the right amount of water at the right time.
In Dubai, the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) has implemented a blockchain-based smart water network initiative as part of its broader smart city strategy. This project integrates blockchain technology with IoT sensors to monitor water usage in real time, manage distribution, and detect leaks. The decentralized ledger ensures data integrity and transparency, enabling more efficient water management and reduced waste. DEWA’s initiative aims to improve sustainability and resource management in the rapidly growing city, highlighting the potential of blockchain to support urban water management and conservation efforts.
Community participation and ownership
Through blockchain, individuals can directly control and monetize their access to water resources, eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries. This direct control model allows local communities to make collective and transparent decisions about their water use. By managing their water directly from the source, communities can tailor water management practices to their specific needs, promoting equitable distribution and encouraging a sense of accountability and stewardship.
Additionally, future models could allow people to monetize their access to water through web3 technologies. For example, a community-to-business (C2B) model could allow people to sell water directly to companies. In this model, people do not have to own the water directly, but can profit by staking their tokens during event sales pools. This approach not only supports sustainable water management, but also creates economic opportunities for community members. Additionally, a “Burn to Secure” protocol can be used to provide water allocation rights. This protocol provides a true sense of water security and financial opportunity by allowing people to redeem their rights. This system not only secures future water allocations, but also increases token scarcity and value.
Additionally, a pure sense of investment is achieved through investments in water sources. This leads to potential financial returns and dividends by addressing the inefficiencies in water supply mentioned above. By investing to finance infrastructure projects, such as building factories and improving distribution systems, more water can be brought to communities, creating additional economic opportunities.
Monetizing water access through the C2B model, the “Burn to Secure” protocol, and investments in water sources all generate economic benefits for the community, promoting a more equitable and efficient water management system.
Overcoming challenges
While blockchain technology has the potential to improve water management, there are challenges to its adoption. The complexity of blockchain systems and the need for technological infrastructure can be barriers, especially in developing regions. Additionally, there are concerns about the significant energy consumption of blockchain networks. However, technological advances and the development of more energy-efficient blockchain solutions are helping to alleviate these concerns. Additionally, education and capacity building are key to ensuring stakeholders understand how to effectively use blockchain technology. Governments, NGOs, and private sector partners need to work together to provide training and support to communities and water management authorities.
Blockchain technology offers a practical and effective means to improve water management. In addition to addressing inefficiencies, blockchain empowers communities, promotes sustainable practices, and opens up new economic opportunities through models like community-to-business (C2B). As we face the growing challenges of climate change and population growth, blockchain is not only an innovative solution, but represents a fundamental shift in the way we manage and value water resources. Adopting blockchain in water management is essential to creating a sustainable and equitable future by changing the way we interact with and protect our most vital resource.

Jean-Hugues Gavarini
Jean-Hugues Gavarini is the CEO and co-founder of LAKE (LAK3), a real-world asset company leveraging blockchain technology to decentralize access to the global water economy. LAKE aims to ensure access to clean water for all, protect water resources, and deliver water to those in need through innovative technologies. Jean-Hugues has a diverse career spanning the luxury, fashion, and footwear industries. His career path includes notable successes at Mellow Yellow, Cremieux, and Tod’s. Raised between Silicon Valley and the French Alps, Jean-Hugues has always been immersed in technology and freshwater resources. In 2018, Jean became the CEO of Lanikea Waters, a water solutions entity based in the French Alps. In 2019, the concept of LAKE was born, embodying his commitment to innovation and sustainability.
News
Blockchain and AI Expo 2024

With rapid advances in the world of AI and blockchain, there are opportunities to leverage the security and transparency features of blockchain to improve the reliability and trust of AI systems and data transactions.
Explore the synergy of these advanced technologies in virtual mode Blockchain and AI Expowhich takes place on October 31, 2024 TO 10:00 GMT.
The event features cutting-edge presentations led by leading experts in evolving fields. Presentations are set to explore opportunities and challenges in the fusion of blockchain and AI, real-world applications, ethics, innovations in environmental sustainability, and more!
Gain a comprehensive understanding of how these technologies can synergistically drive innovation, optimize operations, and promote strategic growth opportunities. Develop your knowledge to facilitate informed decision making and give your company a competitive edge in the growing technology landscape.
News
Nigeria Eyes National Blockchain Nigerium for Data Sovereignty

Nigeria is keeping an eye on a new native blockchain network to protect the country’s data sovereignty.
According to local media, a team from the University of Hertfordshire has proposed the new blockchain, Nigeriato the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA).
Chanu Kuppuswamy, who leads the team, argued that relying on blockchain networks whose developers are located in other regions poses national security risks to the Nigerian government. He further said that Nigerium would allow the West African nation to customize the network to meet specific needs, while also promoting data sovereignty.
In his presentation, Chanu cited the recent migration of Ethereum to test of participation (PoS) consensus as an instance in which no Nigerians were involved but whose impact is far-reaching.
“Developing an indigenous blockchain like Nigerium is a significant step towards achieving data sovereignty and promoting trust in digital transactions in Nigeria,” he said.
While receiving the proposals in Abuja, NITDA’s Kashifu Abdullahi acknowledged the benefits a local blockchain would bring to Nigeria, including increased security of citizens’ data.
However, a NITDA spokesperson later clarified that Nigerium is still at the proposal stage and that the government has not yet decided whether to proceed or not.
“The committee is still discussing the possibility with stakeholders. Even if a decision is finally made, there is no guarantee that the name will be Nigerium,” the spokesperson told the media.
Nigerium’s reception in the country has been mixed. Some, like financial analyst Olumide Adesina, To say the network is “dead on arrival”. He believes the Nigerian government’s poor record in following through on its big technology plans will claim another victim. He pointed to the eNaira as a missed opportunity whose chances of success were much higher than those of Nigerium.
Others welcomed the proposal. Chimezie Chuta, who chairs the renewed The Nigerian Blockchain Policy Committee is “extremely optimistic“that Nigerium will be more successful than eNaira.
Speaking to a local news agency, Chuta stressed that eNaira failed because the central bank initiated the project on its own, without involving any stakeholders.
“They just cooked it and expected everyone to like it. [With Nigerium]there will be a lot of collaboration,” he said.
Registration of property title, digital identity and Certificate Verification are among the use cases that Nigerium is expected to initially target. However, Nigeria has already made progress in some of these fields through public blockchains.
SPPG, a leading school in governance and politics, announced in May the country’s first blockchain certificate verification system. Built on the The BSV BlockchainIt was developed in collaboration with the blockchain data recording company VX Technologies and local lender Sterling Bank.
Watch: The Future Has Already Arrived in Nigeria
 Italian: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M40GXUUauLU width=”560″ height=”315″ frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
Italian: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M40GXUUauLU width=”560″ height=”315″ frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
New to blockchain? Check out CoinGeek Blockchain for Beginners section, the definitive guide to learn more about blockchain technology.
News
Cambodian CBDC Developer to Build Palau Bond Market on Blockchain: Report

A Japanese fintech developer will build a blockchain-based bond market gateway for Palau, aiming to launch a trial in 2024 and a full launch the following year.
Japanese fintech developer Suramitsubest known for developing a central bank digital currency (CBDC) for Cambodia, is intended to build a Blockchain-gateway to the bond market based on the Pacific island nation of Palau, Nikkei He learned.
Soramitsu won the contract and plans to introduce the market on a trial basis in fiscal 2024, with a full launch scheduled for the following year, allowing the Palauan government to issue bonds to individual investors and efficiently manage principal and interest payments, according to the report.
The total cost of the project is estimated at several hundred million yen ($1.2 million to $5.6 million), less than half the cost of a non-blockchain alternative, people familiar with the matter said. The project has reportedly received support from Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, with Japan’s foreign and finance ministries providing strategic and management advice on the project.
Soramitsu’s successful development of Cambodia’s CBDC in 2020 has boosted its reputation, with the digital currency’s popularity soaring, with over 10 million accounts opened by December 2023, representing 60% of Cambodia’s population. Following this, Cambodia’s central bank governor Chea Serey indicated intends to expand the reach of its CBDC internationally, particularly through collaboration with UnionPay International, the Chinese card payment service, and other global partners.
While Soramitsu’s work in Cambodia has been well received, the long-term popularity of CBDCs remains to be seen. As of late June, crypto.news reported a sharp drop in activity in India’s digital currency, the e-rupee, after local banks stopped artificially inflating its values.
According to people familiar with the matter, the Reserve Bank of India managed to hit the 1 million retail transaction milestone last December only after the metrics were artificially infiltrated by local banks, which offered incentives to retail users and paid a portion of the bank’s employees’ salaries using the digital currency.
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago“Captain Tsubasa – RIVALS” launches on Oasys Blockchain
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoHistoric steps for US cryptocurrencies! With a shocking majority vote!🚨
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoIs Emorya the next gem💎 of this Bitcoin bull run?
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSolana Surpasses Ethereum and Polygon as the Fastest Blockchain ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoNexus Chain – Ethereum L2 with the GREATEST Potential?
-
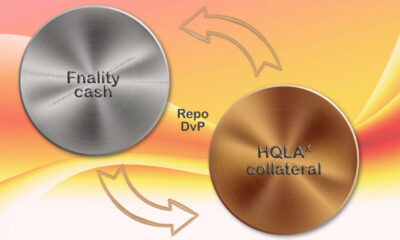
 News1 year ago
News1 year agoFnality, HQLAᵡ aims to launch blockchain intraday repositories this year – Ledger Insights
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoScaling Ethereum with L2s damaged its Tokenomics. Is it possible to repair it?
-

 Regulation1 year ago
Regulation1 year agoFinancial Intelligence Unit imposes ₹18.82 crore fine on cryptocurrency exchange Binance for violating anti-money laundering norms
-

 Bitcoin1 year ago
Bitcoin1 year agoBitcoin Drops to $60K, Threatening to Derail Prices of Ether, Solana, XRP, Dogecoin, and Shiba Inu ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSendBlocks Debuts with Major Support to Improve Blockchain Data Management











