News
Blockchain in Finance: Beyond Cryptocurrency Applications

Look beyond the cryptocurrency hype and discover how to integrate blockchain into financial processes, from trading to loyalty programs
While the excitement around cryptocurrency and bitcoin may have cooled, blockchain adoption shows no signs of slowing down. By 2030, PwC expects that 20% of the world’s economic infrastructure could run on blockchain-based systems, making its role in finance particularly important. Let’s look at the 10 low-hanging fruit for blockchain and finance and how they could transform financial operations.
1. Simplifying trade finance processes
Imagine you are a trader navigating the complex waters of global trade. Every shipment involves a barrage of paperwork, from letters of credit to bills of lading. Enter blockchain. Think of it as an incorruptible digital ledger distributed across multiple nodes. Every transaction, from purchase orders to invoices, is recorded as an immutable block. This eliminates the need for manual verification, saving time and reducing the risk of errors or fraud.
Smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements triggered by predefined conditions, automate processes such as releasing payment upon confirmation of delivery. With blockchain, trade finance becomes a seamless and transparent ecosystem that accelerates transactions and strengthens trust between parties.
2. Improve wealth management
Managing assets can feel like herding cats: tracking ownership, verifying authenticity, and ensuring compliance. Blockchain revolutionizes all of this by creating a tamper-proof ownership ledger.
You can store your assets (real estate, stocks, or artwork) as digital tokens on a blockchain. Each token contains immutable data, including ownership history and provenance. This transparency fights fraud and simplifies transactions, enabling real-time settlements and fractional ownership. Additionally, smart contracts automate processes such as dividend distributions or asset transfers, reducing administrative expenses.
3. Make supply chain financing more transparent
In today’s interconnected world, supply chains resemble a tangled web of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Tracking the flow of assets and finances can feel like stumbling in the dark.
Blockchain highlights this complexity. It converts supply chains into a series of interconnected blocks, each containing crucial data: product origins, shipping routes and payment details. This transparent registry ensures accountability and traceability at every stage, mitigating risks such as counterfeiting or unethical practices.
4. Accelerate cross-border payments
Sometimes, sending money across borders can feel like a journey through a bureaucratic quagmire: long processing times, high fees, and uncertain exchange rates. Blockchain offers a shortcut into this maze. Essentially, it enables peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Each transaction, recorded on a distributed ledger, is immutable and transparent, eliminating the need for reconciliation between multiple banks.
Cryptographic algorithms ensure security and privacy, protecting sensitive data from prying eyes. Smart contracts facilitate instant settlement, bypassing traditional clearinghouses and reducing transaction costs. This makes cross-border payments faster, cheaper and more reliable, enabling individuals and businesses to participate in the global economy with ease.
5. Transforming financial agreements with smart contracts
These self-executing contracts are encoded with predefined conditions and distributed on a blockchain network. When these conditions are met, the contract is automatically executed, facilitating transactions or enforcing agreements.
Let’s say you’re entering into a loan agreement. With a smart contract, the terms of the loan, such as the repayment schedule and interest rates, are encoded in the contract. Once both parties agree and the conditions are met, the contract is automatically executed, releasing funds to the borrower and guaranteeing repayment according to the agreed terms.
The technical brilliance behind smart contracts lies in their code, which is immutable and tamper-proof once deployed on the blockchain. This ensures that the terms of the contract cannot be altered, providing high security and trust between the parties. They offer unparalleled transparency, as every step of the agreement is recorded on the blockchain and visible to all parties involved.
6. Verification of customer identity in financial services
Blockchain offers a secure and efficient solution to the age-old challenge of verifying customer identity in financial services. Your identity information, such as name, address and other relevant data, is encrypted and stored on a blockchain network.
Whenever you interact with a financial institution, you can provide access to your encrypted identity data. Using cryptographic keys, the institution can instantly verify your identity without cumbersome paperwork or manual verification processes.
Blockchain ensures the security and privacy of your identity data, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to access or tamper with your information. It also enables self-sovereign identity, giving you full control over your identity data and allowing you to choose when and how to share it with financial institutions.
Financial institutions that adopt this technology can streamline onboarding processes, reduce the risk of identity theft and fraud, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
7. Regulatory compliance assistance
Blockchain cryptographic algorithms guarantee the security and integrity of transaction data, protecting them from unauthorized access or tampering. Every transaction conducted on the network is recorded in a transparent and immutable register. This registry gives regulators real-time access to accurate and verifiable transaction data, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
Smart contracts, implemented on the blockchain, can automate compliance processes by automatically enforcing regulatory requirements. For example, they can ensure that transactions adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations or automatically report suspicious activity to regulators.
Leveraging blockchain in finance can streamline regulatory compliance processes, reduce costs, and build trust with regulators and customers.
8. Enabling loyalty programs
Blockchain in finance can represent an innovative solution for managing loyalty programs. Loyalty points or rewards are tokenized and recorded on a blockchain network. Every time you earn or redeem points, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accuracy in reward management.
Additionally, blockchain enables interoperability between different loyalty programs, allowing users to seamlessly earn and redeem points across multiple platforms. Its decentralized nature eliminates the risk of fraud or manipulation, ensuring the integrity of loyalty programs. Smart contracts can automate processes such as reward distribution and expiration, providing users with a smooth and efficient experience.
9. Processing of insurance claims
Blockchain acts as a distributed ledger where information about insurance policies, claims, and transactions is recorded in an immutable and tamper-proof manner. When you initiate a claim, the relevant details are recorded on the blockchain, including your identity details, the nature of the claim, and any supporting documentation.
With smart contracts, you can trigger the release of funds once they are satisfied. For example, suppose an insurance policy covers property damage due to natural disasters. In that case, the smart contract can automatically release the funds to the claimant once the damage has been verified by a trusted source.
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that all parties involved in the claims process, including the claimant, the insurer and all third-party validators, have access to the same information in real time. This transparency reduces the likelihood of disputes and speeds up the claims settlement process.
10. Strengthening credit risk models
Blockchain Technology has the potential to transform credit risk modeling by offering a comprehensive and transparent view of borrowers’ financial history and behavior. It is a decentralized ledger where financial transactions, including loan repayments, credit card payments, and other financial activities, are recorded in real time. Each transaction is cryptographically protected and linked to the borrower’s unique identifier, such as a public key.
By analyzing transaction history stored on the blockchain, lenders can gain insights into borrowers’ creditworthiness and risk profiles. Traditional credit risk models rely on historical credit data from centralized credit bureaus, which may be limited or outdated. In contrast, blockchain offers a more complete and up-to-date picture of borrowers’ financial behavior.
For example, if a borrower fails to repay the loan on time, the smart contract can automatically trigger penalties or initiate debt collection procedures.
There’s no time like now: adopting Blockchain will future-proof your business
Despite promising use cases for blockchain in finance, adoption has lagged. Most regulatory regimes tend to take a conservative approach to the technology, resulting in legal or tax barriers. Blockchain in finance also requires widespread adoption of decentralized infrastructure, a fundamental shift in information technology systems. However, decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to thrive, signaling continued demand and opportunities for institutions that can capitalize blockchain beyond cryptocurrency.
News
Blockchain Technology Will Transform Water Access and Management Globally

Disclosure: The views and opinions expressed here are solely those of the author and do not represent the views and opinions of the crypto.news editorial team.
Access to clean water is a basic human need, yet billions of people around the world still struggle to get it. According to the World Health Organization, over 2 billion people live in countries suffering from severe water stress, and this number is expected to continue to grow due to climate change and population growth.
Traditional water management systems have struggled to address these challenges, often hampered by inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and misallocation of resources. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to these challenges, providing equitable access and sustainable use of this crucial resource.
The current state of water management
Water management today faces several pressing issues. Inefficiencies in water supply, distribution, and use, coupled with a lack of real-time monitoring, often result in resource waste and misallocation. Many water sources fail to realize their full potential due to infrastructure and financing shortfalls. For example, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) report indicated that the United States would need to invest $625 billion over the next 20 years to repair, maintain and improve the country’s drinking water infrastructure due to aging pipes and other infrastructure problems. Additionally, in the United States alone, household leaks can to waste nearly 900 billion gallons of water per year nationwide. This is equivalent to the annual domestic water consumption of nearly 11 million homes.
Furthermore, corruption and mismanagement of water resources can cause unequal distribution, with disadvantaged communities often bearing the brunt of water scarcity. For example, South Africa is struggling with myriad challenges to its water security: drought, inadequate water conservation measures, outdated infrastructure, and unequal access to water resources. The country faces significant water scarcity, with demand expected to outstrip supply by 2030, creating a projected gap of 17%.
Furthermore, the global water industry is highly monopolized, with a few key players controlling a significant share of the market. These companies exert substantial influence over the water supply chain, often prioritizing profit over equitable distribution and environmental responsibility. This concentration of power can lead to inflated prices and limited access for vulnerable populations. The global bottled water market alone is projected to reach $509.18 billion by 2030, with these large companies capturing a significant share of revenue. This monopolization exacerbates existing inequalities in water access and highlights the need for more decentralized and community-driven water management solutions.
Source: Grand View Search
The potential of blockchain in water management
Blockchain technology can address these issues by providing a transparent, secure, and decentralized platform for water resource management. This approach offers several advantages:
- Transparency and accountability. Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that all transactions and data entries are transparent and cannot be changed once recorded. This transparency can reduce corruption and ensure that water resources are allocated fairly and efficiently. For example, blockchain can be used to track water usage from source to end user, providing a clear record of how water is distributed and used. This level of transparency can help hold authorities accountable and manage water resources sustainably.
- Efficient resource management. Blockchain can facilitate the creation of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into the code. These contracts can automate water distribution based on real-time data, directing water to where it is needed most. For example, smart contracts could be used to manage urban water supply systems, automatically adjusting water distribution based on real-time consumption patterns and demand. This can help optimize water use, reduce waste, and ensure that households and businesses receive the right amount of water at the right time.
In Dubai, the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) has implemented a blockchain-based smart water network initiative as part of its broader smart city strategy. This project integrates blockchain technology with IoT sensors to monitor water usage in real time, manage distribution, and detect leaks. The decentralized ledger ensures data integrity and transparency, enabling more efficient water management and reduced waste. DEWA’s initiative aims to improve sustainability and resource management in the rapidly growing city, highlighting the potential of blockchain to support urban water management and conservation efforts.
Community participation and ownership
Through blockchain, individuals can directly control and monetize their access to water resources, eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries. This direct control model allows local communities to make collective and transparent decisions about their water use. By managing their water directly from the source, communities can tailor water management practices to their specific needs, promoting equitable distribution and encouraging a sense of accountability and stewardship.
Additionally, future models could allow people to monetize their access to water through web3 technologies. For example, a community-to-business (C2B) model could allow people to sell water directly to companies. In this model, people do not have to own the water directly, but can profit by staking their tokens during event sales pools. This approach not only supports sustainable water management, but also creates economic opportunities for community members. Additionally, a “Burn to Secure” protocol can be used to provide water allocation rights. This protocol provides a true sense of water security and financial opportunity by allowing people to redeem their rights. This system not only secures future water allocations, but also increases token scarcity and value.
Additionally, a pure sense of investment is achieved through investments in water sources. This leads to potential financial returns and dividends by addressing the inefficiencies in water supply mentioned above. By investing to finance infrastructure projects, such as building factories and improving distribution systems, more water can be brought to communities, creating additional economic opportunities.
Monetizing water access through the C2B model, the “Burn to Secure” protocol, and investments in water sources all generate economic benefits for the community, promoting a more equitable and efficient water management system.
Overcoming challenges
While blockchain technology has the potential to improve water management, there are challenges to its adoption. The complexity of blockchain systems and the need for technological infrastructure can be barriers, especially in developing regions. Additionally, there are concerns about the significant energy consumption of blockchain networks. However, technological advances and the development of more energy-efficient blockchain solutions are helping to alleviate these concerns. Additionally, education and capacity building are key to ensuring stakeholders understand how to effectively use blockchain technology. Governments, NGOs, and private sector partners need to work together to provide training and support to communities and water management authorities.
Blockchain technology offers a practical and effective means to improve water management. In addition to addressing inefficiencies, blockchain empowers communities, promotes sustainable practices, and opens up new economic opportunities through models like community-to-business (C2B). As we face the growing challenges of climate change and population growth, blockchain is not only an innovative solution, but represents a fundamental shift in the way we manage and value water resources. Adopting blockchain in water management is essential to creating a sustainable and equitable future by changing the way we interact with and protect our most vital resource.

Jean-Hugues Gavarini
Jean-Hugues Gavarini is the CEO and co-founder of LAKE (LAK3), a real-world asset company leveraging blockchain technology to decentralize access to the global water economy. LAKE aims to ensure access to clean water for all, protect water resources, and deliver water to those in need through innovative technologies. Jean-Hugues has a diverse career spanning the luxury, fashion, and footwear industries. His career path includes notable successes at Mellow Yellow, Cremieux, and Tod’s. Raised between Silicon Valley and the French Alps, Jean-Hugues has always been immersed in technology and freshwater resources. In 2018, Jean became the CEO of Lanikea Waters, a water solutions entity based in the French Alps. In 2019, the concept of LAKE was born, embodying his commitment to innovation and sustainability.
News
Blockchain and AI Expo 2024

With rapid advances in the world of AI and blockchain, there are opportunities to leverage the security and transparency features of blockchain to improve the reliability and trust of AI systems and data transactions.
Explore the synergy of these advanced technologies in virtual mode Blockchain and AI Expowhich takes place on October 31, 2024 TO 10:00 GMT.
The event features cutting-edge presentations led by leading experts in evolving fields. Presentations are set to explore opportunities and challenges in the fusion of blockchain and AI, real-world applications, ethics, innovations in environmental sustainability, and more!
Gain a comprehensive understanding of how these technologies can synergistically drive innovation, optimize operations, and promote strategic growth opportunities. Develop your knowledge to facilitate informed decision making and give your company a competitive edge in the growing technology landscape.
News
Nigeria Eyes National Blockchain Nigerium for Data Sovereignty

Nigeria is keeping an eye on a new native blockchain network to protect the country’s data sovereignty.
According to local media, a team from the University of Hertfordshire has proposed the new blockchain, Nigeriato the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA).
Chanu Kuppuswamy, who leads the team, argued that relying on blockchain networks whose developers are located in other regions poses national security risks to the Nigerian government. He further said that Nigerium would allow the West African nation to customize the network to meet specific needs, while also promoting data sovereignty.
In his presentation, Chanu cited the recent migration of Ethereum to test of participation (PoS) consensus as an instance in which no Nigerians were involved but whose impact is far-reaching.
“Developing an indigenous blockchain like Nigerium is a significant step towards achieving data sovereignty and promoting trust in digital transactions in Nigeria,” he said.
While receiving the proposals in Abuja, NITDA’s Kashifu Abdullahi acknowledged the benefits a local blockchain would bring to Nigeria, including increased security of citizens’ data.
However, a NITDA spokesperson later clarified that Nigerium is still at the proposal stage and that the government has not yet decided whether to proceed or not.
“The committee is still discussing the possibility with stakeholders. Even if a decision is finally made, there is no guarantee that the name will be Nigerium,” the spokesperson told the media.
Nigerium’s reception in the country has been mixed. Some, like financial analyst Olumide Adesina, To say the network is “dead on arrival”. He believes the Nigerian government’s poor record in following through on its big technology plans will claim another victim. He pointed to the eNaira as a missed opportunity whose chances of success were much higher than those of Nigerium.
Others welcomed the proposal. Chimezie Chuta, who chairs the renewed The Nigerian Blockchain Policy Committee is “extremely optimistic“that Nigerium will be more successful than eNaira.
Speaking to a local news agency, Chuta stressed that eNaira failed because the central bank initiated the project on its own, without involving any stakeholders.
“They just cooked it and expected everyone to like it. [With Nigerium]there will be a lot of collaboration,” he said.
Registration of property title, digital identity and Certificate Verification are among the use cases that Nigerium is expected to initially target. However, Nigeria has already made progress in some of these fields through public blockchains.
SPPG, a leading school in governance and politics, announced in May the country’s first blockchain certificate verification system. Built on the The BSV BlockchainIt was developed in collaboration with the blockchain data recording company VX Technologies and local lender Sterling Bank.
Watch: The Future Has Already Arrived in Nigeria
 Italian: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M40GXUUauLU width=”560″ height=”315″ frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
Italian: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M40GXUUauLU width=”560″ height=”315″ frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
New to blockchain? Check out CoinGeek Blockchain for Beginners section, the definitive guide to learn more about blockchain technology.
News
Cambodian CBDC Developer to Build Palau Bond Market on Blockchain: Report

A Japanese fintech developer will build a blockchain-based bond market gateway for Palau, aiming to launch a trial in 2024 and a full launch the following year.
Japanese fintech developer Suramitsubest known for developing a central bank digital currency (CBDC) for Cambodia, is intended to build a Blockchain-gateway to the bond market based on the Pacific island nation of Palau, Nikkei He learned.
Soramitsu won the contract and plans to introduce the market on a trial basis in fiscal 2024, with a full launch scheduled for the following year, allowing the Palauan government to issue bonds to individual investors and efficiently manage principal and interest payments, according to the report.
The total cost of the project is estimated at several hundred million yen ($1.2 million to $5.6 million), less than half the cost of a non-blockchain alternative, people familiar with the matter said. The project has reportedly received support from Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, with Japan’s foreign and finance ministries providing strategic and management advice on the project.
Soramitsu’s successful development of Cambodia’s CBDC in 2020 has boosted its reputation, with the digital currency’s popularity soaring, with over 10 million accounts opened by December 2023, representing 60% of Cambodia’s population. Following this, Cambodia’s central bank governor Chea Serey indicated intends to expand the reach of its CBDC internationally, particularly through collaboration with UnionPay International, the Chinese card payment service, and other global partners.
While Soramitsu’s work in Cambodia has been well received, the long-term popularity of CBDCs remains to be seen. As of late June, crypto.news reported a sharp drop in activity in India’s digital currency, the e-rupee, after local banks stopped artificially inflating its values.
According to people familiar with the matter, the Reserve Bank of India managed to hit the 1 million retail transaction milestone last December only after the metrics were artificially infiltrated by local banks, which offered incentives to retail users and paid a portion of the bank’s employees’ salaries using the digital currency.
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year ago“Captain Tsubasa – RIVALS” launches on Oasys Blockchain
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSolana ranks the fastest blockchain in the world, surpassing Ethereum, Polygon ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoHistoric steps for US cryptocurrencies! With a shocking majority vote!🚨
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoIs Emorya the next gem💎 of this Bitcoin bull run?
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSolana Surpasses Ethereum and Polygon as the Fastest Blockchain ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 Videos1 year ago
Videos1 year agoNexus Chain – Ethereum L2 with the GREATEST Potential?
-
 News1 year ago
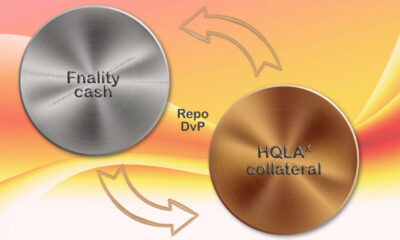
News1 year agoFnality, HQLAᵡ aims to launch blockchain intraday repositories this year – Ledger Insights
-

 Ethereum1 year ago
Ethereum1 year agoScaling Ethereum with L2s damaged its Tokenomics. Is it possible to repair it?
-

 Regulation1 year ago
Regulation1 year agoFinancial Intelligence Unit imposes ₹18.82 crore fine on cryptocurrency exchange Binance for violating anti-money laundering norms
-

 Bitcoin1 year ago
Bitcoin1 year agoBitcoin Drops to $60K, Threatening to Derail Prices of Ether, Solana, XRP, Dogecoin, and Shiba Inu ⋆ ZyCrypto
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoSendBlocks Debuts with Major Support to Improve Blockchain Data Management










